CBSE Class 10 Science Chapter 9 Light Reflection and Refraction is an important topic to understand the basics of light. This post includes important questions and answers on topics ranging from ray optics, spherical mirrors, refraction of light, mirror formulas, and numerical problems for exam preparation. Get detailed explanations with diagrams for a better understanding of light reflection and refraction concepts.

| Subject | Science (Physics) |
| Class | 10 |
| Board | CBSE |
| Chapter No. | 9 |
| Chapter Name | Light Reflection and Refraction |
| Type | Important Questions and Answers |
| Session | 2024-25 |
Light Reflection and Refraction Class 10 Important Questions Answers
Q. No. 1) Multiple Choice Questions (MCQs)
i. The angle of incidence from air to glass at point O on the hemispherical glass slab is _____.
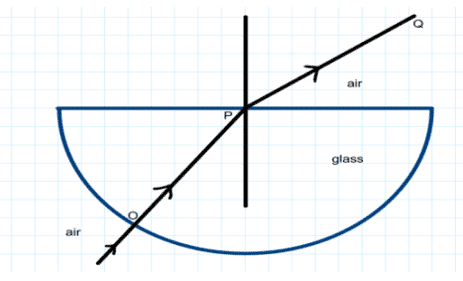
a. 45°
b. 0°
c. 90°
d. 180°
Ans. Option (b)
ii. Rays from the sun converge at a point 15 cm in front of a concave mirror. Where should an object be placed so that the size of its image is equal to the size of the object?
a. 30 cm in front of the mirror
b. 15 cm in front of the mirror
c. Between 15 cm and 30 cm in front of the mirror
d. More than 30 cm in front of the mirror
Ans. Option (a) [Sun rays converge at 15 cm means the focal length is 15 cm. So image is placed at 2f = 2 x 15 = 30 cm]
iii. Examine the below figure and state which of the following options is correct.
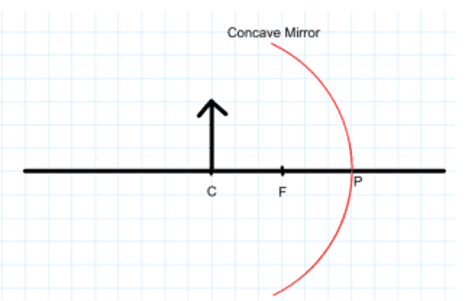
(one small box in the figure is equal to 1 cm)
a. The mirror has a focal length of -6 cm and will produce an image of magnification +1.
b. The mirror has a focal length of -3 cm and will produce an image of magnification -1
c. The mirror has a focal length of -3 cm and will produce an image of magnification +1
d. The mirror has a focal length of -6 cm and will produce an image of magnification -1
Ans. Option (b)
iv. While looking at the below diagram, Nalini concluded the following:
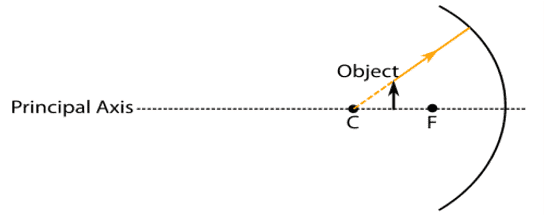
- The image of the object will be a virtual one.
- The reflected ray will travel along the same path as the incident ray but in the opposite direction.
- The image of the object will be inverted.
- This is a concave mirror and hence the focal length will be negative.
Which one of the above statements is correct?
a. I and II
b. I and III
c. II, III and IV
d. I, II, III and IV
Ans. Option (c)
v. Which of the following mirror is used by a dentist to examine a small cavity in a patient’s teeth?
a. Convex mirror
b. Plane mirror
c. Concave mirror
d. Any spherical mirror
Ans. Option (c)
vi. In the diagram shown below, a light ray is incident on a convex mirror.
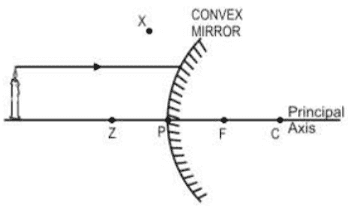
Through which point will the ray travel after reflecting off the mirror?
a. C
b. F
c. X
d. Z
Ans. Option (c)
vii. Which of the following can make a parallel beam of light when light from a point source is incident on it?
a. Concave mirror as well as a convex lens.
b. Convex mirror as well as a concave lens.
c. Two plane mirrors placed at 90° to each other.
d. Concave mirror as well as a concave lens.
Ans. Option (a)
viii. Magnification produced by a rearview mirror fitted in vehicles
a. Is less than 1
b. Is more than 1
c. Is equal to one
d. Can be more than or less than 1 depending upon the position of the object in front of it
Ans. Option (a)
ix. In the diagram shown below, a beam of light is traveling from inside a glass slab to air. Which of the marked paths will the ray of light take as it emerges from the glass slab?
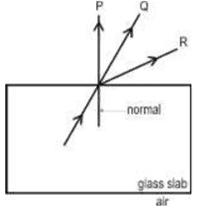
a. P
b. Q
c. R
d. None of them as light splits into its many colors
Ans. Option (c)
x. The figure below shows a ray of light as it travels from medium A to medium B. Refractive index of medium B relative to medium A is
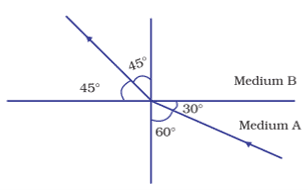
a. √3/√2
b. √2/√3
c. 1/√2
d. √2
Ans. Option (a)
[∠i=60°, ∠r=45°
∴ Refractive index of B w.r.t A (nBA) = sin i/sin r = sin 60°/sin 45° = (√3/2)/(1/√2) = √3/√2]
xi. In the below diagram light is traveling through different media. It is noted by a scientist that ∠1 = ∠3 = ∠4 but ∠2 = ∠1. Which of the following statement would be correct?

a. Medium 1 is denser than medium 3 but its density is equal to medium 2.
b. Medium 2 is the rarest medium.
c. Medium 3 is denser than medium 1.
d. Medium 1 and 3 are essentially the same medium, but medium 2 is denser than 1 and 3.
Ans. Option (d)
xii. As a ray of light entered medium P from medium Q, its velocity increased.
What can be said about the refractive index of medium P as compared to that of medium Q?
a. It is lower.
b. It is higher.
c. It is the same.
d. Nothing can be said without knowing what medium P and medium Q are.
Ans. Option (a) [More refractive index means less speed and vice-versa]
xiii. The refractive index of flint glass is 1.65 and that for alcohol is 1.36 with respect to air. What is the refractive index of the flint glass with respect to alcohol?
a. 0.82
b. 1.21
c. 1.11
d. 1.01
Ans. Option (b)
[Refractive index of flint glass w.r.t alcohol = RI of flint glass/RI of alcohol = 1.65/1.36 = 1.21]
xiv. Consider these indices of refraction:
- Glass: 1.52
- Air: 1.0003
- Water: 1.333
Based on the refractive indices of three materials, arrange the speed of light through them in decreasing order.
a. The speed of light in water > the speed of light in air > the speed of light in glass
b. The speed of light in glass > the speed of light in water > the speed of light in air
c. The speed of light in air > the speed of light in water > the speed of light in glass
d. The speed of light in glass > the speed of light in air > the speed of light in water
Ans. Option (c)
xv. No matter how far you stand from this spherical mirror, your image always appears erect. The mirror may be:
a. Plane
b. Convex
c. Concave
d. Either plane or convex
Ans. Option (d)
xvi. A small electric lamp is placed at the focus of a convex lens. When the lamp is switched on, the lens will produce:
a. Converging beam of light
b. A parallel beam of light
c. A diverging beam of light
d. A diffused beam of light
Ans. Option (b)
xvii. The below lens has a focal length of 10 cm. The object of height 2 mm is placed at a distance of 5 cm from the pole. Find the height of the image.
a. 4 cm
b. 6.67 mm
c. 4 mm
d. 3.33 mm
Ans. Option (c)

xviii. If the real image of a candle flame formed by a lens is three times the size of the flame and the distance between the lens and image is 80 cm, at what distance should the candle be placed from the lens?
a. -80 cm
b. -40 cm
c. -40/3 cm
d. -80/3 cm
Ans. Option (d)
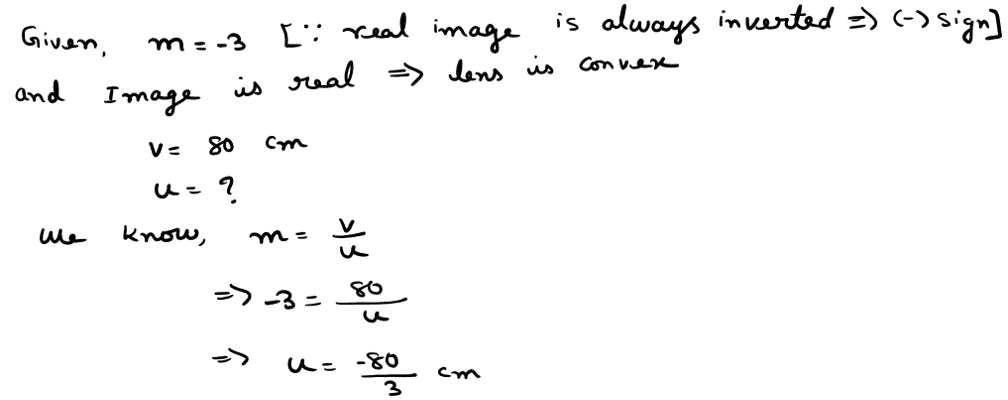
xix. Rajan takes the following two photographs of the text in a book, first while keeping a circular piece of glass on the book and then while holding it at some distance above the book.

Which of the following statements is true about the piece of glass?
a. It is a convex lens as the text is not inverted.
b. It is a concave lens as the text is diminished in size.
c. It is a plane glass disc as there is no difference in the text.
d. It cannot be predicted based on the given information.
Ans. Option (b)
xx. If the power of a lens is - 4.0 D, then it means that the lens is a _____.
a. concave lens of focal length - 50 m
b. convex lens of focal length + 50 cm
c. concave lens of focal length - 25 cm
d. convex lens of focal length - 25 m
Ans. Option (c)

xxi. The following questions consist of two statements - Assertion (A) and Reason (R). Answer these questions by selecting the appropriate options given below:
Assertion (A): Refractive index has no units.
Reason (R): The refractive index is the ratio of two similar quantities.
a. Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A.
b. Both A and R are true and R is not the correct explanation of A.
c. A is true but R is false.
d. A is false but R is true.
Ans. Option (a)
xxii. Assertion (A): A convex mirror is used as a rearview/driver’s mirror.
Reason (R): Convex mirrors have a wider field of view as they are curved outwards. They also give an erect, though the diminished image.
a. Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A.
b. Both A and R are true and R is not the correct explanation of A.
c. A is true but R is false.
d. A is false but R is true.
Ans. Option (a)
Q. No. 2) Case-Based Questions
A. Noor, a young student, was trying to demonstrate some properties of light in her science project work. She kept ‘X’ inside the box (as shown in the figure) and with the help of a laser pointer made light rays pass through the holes on one side of the box. She had a small butter paper screen to see the spots of light being cast as they emerged.
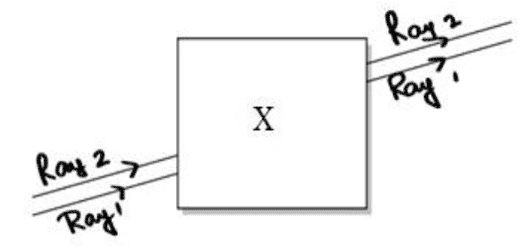
i. What could be the ‘X’ that she placed inside the box to make the rays behave as shown?
a. converging lens
b. parallel-sided glass block
c. plane mirror
d. triangular prism
Ans. Option (b)
ii. She measured the angles of incidence for both the rays on the left side of the box to be 48.6°. She knew the refractive index of the material ‘X’ inside the box was 1.5. What will be the approximate value of the angle of refraction?
a. 45°
b. 40°
c. 30°
d. 60°
(Use the value sin 48.6° = 0.75)
Ans. Option (c).
[ Refractive index = sin i/ sin r
⇒1.5 = sin 48.6°/sin r
⇒1.5 = 0.75/sin r
⇒sin r = 0.75/1.5 = ½ = sin 30
⇒r = 30]
iii. Her friend noted the following observations from this demonstration:
- Glass is optically rarer than air.
- Air and glass allow light to pass through them with the same velocity.
- Air is optically rarer than glass.
- The speed of light through a denser medium is faster than that of a rarer medium.
- The ratio of the sin of the angle of incidence in the first medium to the ratio of the sin of the angle of refraction in the second medium gives the refractive index of the second material with respect to the first one.
Which one of the following combinations of the above statements given below is correct?
a. II, IV, and V are correct.
b. III and IV are correct.
c. I, IV, and V are correct.
d. III and V are correct.
Ans. Option (d)
iv. If the object inside the box was made of a material with a refractive index less than 1.5 then the
a. Lateral shift of the rays would have been less
b. Lateral shift of the rays would have been more
c. Lateral shift of the rays would remain the same as before
d. There is not enough information to comment on any of the above statements
Ans. Option (a)
B. Sumati wanted to see the stars of the night sky. She knows that she needs a telescope to see those distant stars. She finds out that the telescopes, which are made of lenses, are called telescopes and the ones which are made of mirrors are called reflecting telescopes.
So she decided to make a refracting telescope. She bought two lenses L1 and L2 out of which L1 was bigger and L2 was smaller. The larger lens gathers and bends the light, while the smaller lens magnifies the image. Big, thick lenses are more powerful. So to see far away, she needed a big powerful lens. Unfortunately, she realized that a big lens is very heavy.
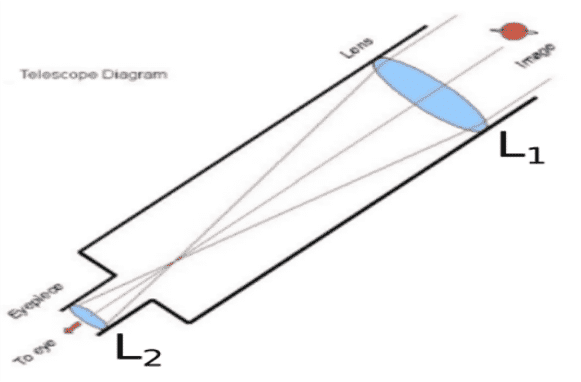
Heavy lenses are hard to make and difficult to hold in the right place. Also since the light is passing through the lens, the surface of the lens has to be extremely smooth. Any flaws in the lens will change the image. It would be like looking through a dirty window.
i. Based on the diagram shown, what kind of lenses would Sumati need to make the telescope?
a. Concave lenses
b. Convex lenses
c. Bifocal lenses
d. Flat lenses
Ans. Option (b)
ii. If the powers of the lenses L1 and L2 are in the ratio of 4:1, what would be the ratio of the focal length of L1 and L2?
a. 4:1
b. 1:4
c. 2:1
d. 1:1
Ans. Option (b)
iii. What is the formula for magnification obtained with a lens?
a. Ratio of the height of the image to the height of object
b. Double the focal length
c. The inverse of the radius of curvature
d. The inverse of the object distance
Ans. Option (a)
iv. Sumati did some preliminary experiments with the lenses and found out that the magnification of the eyepiece (L2) is 3. If in her experiment with L2, she found an image 24 cm from the lens, at what distance did she put the object?
a. 72 cm
b. 12 cm
c. 8 cm
d. 6 cm
Ans. Option (c) [m=v/u]
v. Sumati bought not-so-thick lenses for the telescope and polished them. What advantages, if any, would she have with her choice of lenses?
a. She will not have any advantage as even thicker lenses would give clearer images.
b. Thicker lenses would have made the telescope easier to handle.
c. Not-so-thick lenses would not make the telescope very heavy and also allow a considerable amount of light to pass.
d. Not-so-thick lenses will give her more magnification.
Ans. Option (c)
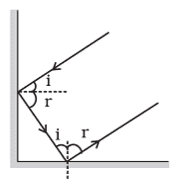
Q. No. 3) Under what condition in an arrangement of two plane mirrors, incident ray and reflected ray will always be parallel to each other, whatever may be the angle of incidence? Show the same with the help of a diagram.
Ans. When two plane mirrors are placed at a right angle to each other then the incident and reflected rays will always be parallel to each other.
Q. No. 4) Both a spherical mirror and a thin spherical lens have a focal length of -15 cm. What type of mirror and lens are these?
Ans. Concave mirror and concave lens.
Q. No. 5) A man standing in front of a spherical mirror, finds his image having a very small head, a fat body, and legs of normal size. What types of mirrors are used in this part?
Ans. A very small head: convex mirror
A fat body: concave mirror
Legs of normal size: plane mirror.
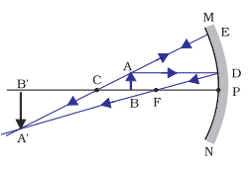
Q. No. 6) The image formed by a concave mirror is observed to be real, inverted, and larger than the object. Where is the object placed?
Ans. Between the principal focus and the center of curvature.
Q. No. 7) Rohit wants to have an erect image of an object using a converging mirror of focal length 40 cm.
a. Specify the range of distance where the object can be placed in front of the mirror. Justify.
b. Will the image be smaller or larger than the object? Draw a ray diagram to show the image formation in this case.
c. Where will the image of this object be, if it is placed 80 cm in front of the mirror?
d. State one use of the mirror based on the above kind of image formation.
Ans. a. The object has to be placed at a distance between 0-40 cm. This is because when the object is placed between F and P, the image formed is virtual, erect, and magnified.
b. Image will be larger than the object.
c. The image will be formed at C.
d. Uses of a concave (converging) mirror:
- Used as a shaving mirror.
- Used by dentists to get an enlarged image of teeth.
- Used in solar furnaces to concentrate sunlight.
- Used in torches, searchlights, and vehicle headlights to get powerful parallel beams of light.
Q. No. 8) Name the mirror that
i. Can give a real as well as a virtual image of an object.
ii. Will always give a virtual image of the same size as the object.
iii. Will always give a virtual and diminished image of an object.
iv. Is used by a doctor in examining teeth.
Ans. i. Concave mirror
ii. Plane mirror
iii. Convex mirror
iv. Concave mirror.
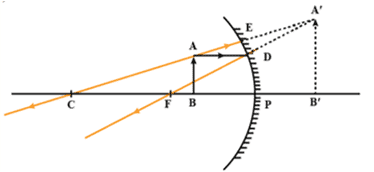
Q. No. 9) The image of an object formed by a mirror is real, inverted, and is of magnification -1. If the image is at a distance of 30 cm from the mirror, where is the object placed? Find the position of the image if the object is now moved 20 cm toward the mirror. What is the nature of the image obtained? Justify your answer with the help of a ray diagram.
Ans.
Nature of image: Virtual, erect, and magnified.

Q. No. 10) Sunita takes a mirror that is depressed at the center and mounts it on a mirror stand. An erect and enlarged image of her face is formed. She places the mirror on a stand along a meter scale at the 15 cm mark. In front of this mirror, she mounts a white screen and moves it back and forth along the meter scale till a sharp, well-defined inverted image of a distant tree is formed on the screen at the 35 cm mark.
i. Name the mirror and find its focal length.
ii. Why does Sunita get a sharp image of the distant building at the 35 cm mark?
Ans. i. Concave mirror.
Focal length (f) = 35-15 = 20 cm.
ii. Sunita gets a sharp image of the distant building at the 35 cm mark because the incident rays parallel to each other after reflection from the concave mirror meet at focus and produce a sharp image at focus.
Q. No. 11) An object of height h is kept at point P in front of a mirror as shown below. The height of the image produced is h’. In the diagram, F is the focus and C is the center of curvature.
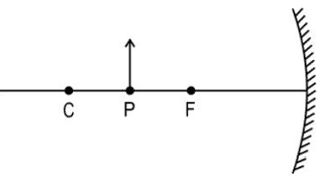
i. If the object is now moved to point C, will the height of the image now produced be less than, equal to, or greater than h’? Give a reason for your answer.
ii. If the focal length of the mirror is 20 cm and the distance between points P and C is 10 cm, determine the distance between the images produced when the object is kept at P and C.
Ans. i. The height of the image produced when the object is at C will be less than h’. The magnification is more when the object is at point P than at C.
ii. Given, f = 20 cm = OF = FC
PC = 10 cm
FP = FC – PC = 20 – 10 = 10 cm
Finding Image distance when the object is at P,
u = OP = OF + FP = 20 + 30 = (-) 30 cm
f = -20 cm
By mirror formula,
1/v + 1/u = 1/f
⇒ 1/v = 1/f – 1/u
⇒ 1/v = 1/-20 – 1/-30 = 1/-20 + 1/30 = -3+2/60 = -1/60
⇒ v = - 60 cm
Finding Image distance when the object is at C,
u = OC = 2f = 2 x 20 = (-) 40 cm
f = -20 cm
By mirror formula,
1/v' + 1/u = 1/f
⇒ 1/v' = 1/f – 1/u
⇒ 1/v' = 1/-20 – 1/-40 = 1/-20 + 1/40 = -2+1/40 = -1/40
⇒ v' = - 40 cm
∴ Required difference = (-60) - (-40) = -60 + 40 = (-) 20 cm [Note: here answer can be given in positive or negative]
Q. No. 12) Write the laws of refraction of light. Explain the same with the help of a ray diagram, when a ray of light passes through a rectangular glass slab.
Or,
Why does a light ray incident on a rectangular glass slab immersed in any medium emerges parallel to itself? Explain using a diagram.
Ans. Laws of refraction of light:
- i. The incident ray, the refracted ray, and the normal to the interface of two transparent media at the point of incidence, all lie in the same plane.
- ii. The ratio of the sine of the angle of incidence to the sine of the angle of refraction is a constant, for the light of a given color and for the given pair of media. This law is also known as Snell’s law of refraction. (This is true for angle 0° < i < 90°)
If i is the angle of incidence and r is the angle of refraction, then,
sin i/sin r = constant
This constant value is called the refractive index of the second medium with respect to the first.
Refraction of light through a rectangular glass slab:
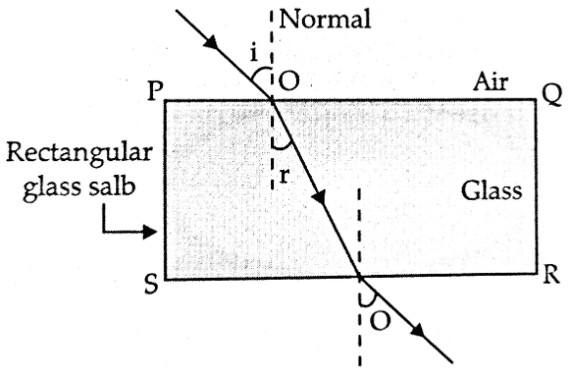
In a rectangular glass slab, the emergent rays are parallel to the incident ray because the extent of bending of the ray of light at the opposite parallel faces of the rectangular glass slab are equal and opposite, so the emergent ray is parallel to the incident ray.
Q. No. 13) For the same angle of incidence in media A, B, and C, the angles of refraction are 20°, 30°, and 40° respectively. In which medium will the velocity of light be maximum? Give a reason in support of your answer.
Ans. From Snell’s law,
n = sin i/sin r = c/v
Since c and sin i are constant, therefore, sin r ∝ v.
Therefore velocity of light is maximum in medium C.
Q. No. 14) Consider the path of a ray of light passing through a rectangular glass slab for different angles of incidence.
i. Which one is greater: the angle of incidence or the angle of emergence?
ii. What happens to the emergent angle on increasing the incident angle at the air-glass interface?
iii. State the conditions when no bending occurs.
Ans. i. ∠i = ∠e.
ii. Angle of emergence also increases.
iii. No bending occurs when:
- The light ray falls along the normal (i.e., ∠i = 0°), Or,
- The refractive index of the two optical media is equal.
Q. No. 15) A coin placed at the bottom of a tank appears to be raised when water is poured into it. Explain.
Ans.
This occurs due to the refraction of light. Here, the ray of light from the coin travels from a denser medium to a rarer medium. In this process, it bends away from the normal. The point from which the refracted rays appear to come gives the apparent position of the coin. As the rays appear to come from a point above the coin, so, the coin seems to be raised.
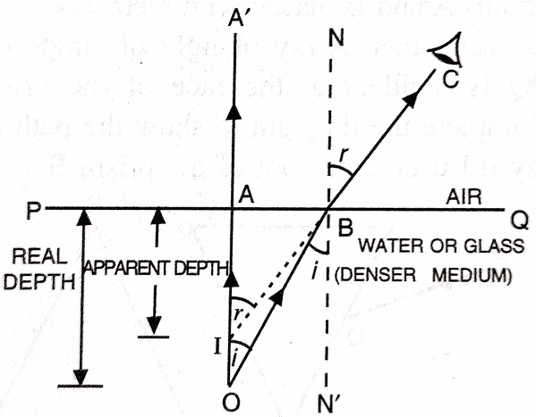
Q. No. 16) i. On entering a medium from the air, the speed of light becomes half of its value in the air. Find the refractive index of that medium with respect to air.
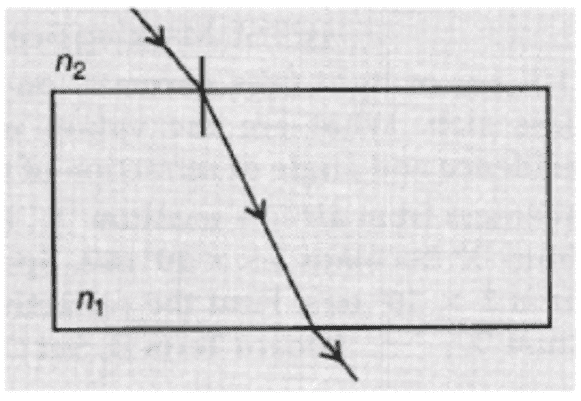
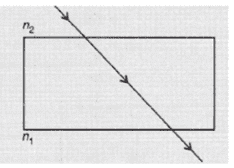
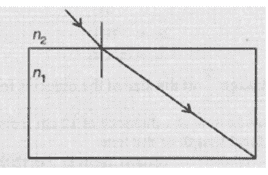
ii. A glass slab made of a material of refractive index n1 is kept in a medium of refractive index n2.
A light ray is incident on the slab. Draw the path of the rays of light emerging from the glass slab, if
a. n1 > n2
b. n1 = n2
c. n1 < n2
Ans. i. Refractive index of a medium (n) = Velocity of light in vacuum (c)/Velocity of light in the medium (v)
Given, v = c/2
Therefore, n = c/v = c/(c/2) = 2
ii. a. The ray moves towards the normal.
b. The ray moves undeviated.
c. The ray moves away from the normal.
Q. No. 17) How is the refractive index of a medium related to the speed of light? Obtain an expression for the refractive index of a medium with respect to another in terms of the speed of light in these two media.
Ans. The refractive index of a medium (n) = Velocity of light in vacuum (c)/Velocity of light in the medium (v)
n = c/v
n1 = refractive index of the first medium
n2 = refractive index of the second medium
v1 = velocity of light in the first medium
v2 = velocity of light in the second medium
For the first medium, n1 = c/v1
For the second medium, n2 = c/v2
n21 = n2/n1 = c/v2/c/v1 = v1/v2
Q. No. 18) Refractive index of two material mediums X and Y are 1.3 and 1.5 respectively. In which of the two, the light would travel faster?
Ans. In medium X because of the lower value of the refractive index.
Q. No. 19) The refractive indices of three media are given below:
| Medium | Refractive index |
| A | 1.6 |
| B | 1.8 |
| C | 1.5 |
A ray of light is traveling from A to B and another ray is traveling from B to C.
(a) In which of the two cases the refracted ray bends towards the normal?
(b) In which case does the speed of light increase in the second medium?
Give reasons for your answer.
Ans. (a) When light travels from an optically rarer medium to an optically denser medium it moves toward the normal. Since nB > nA hence the light ray will bend towards the normal on passing from medium A to B.
(b) The speed of the light will increase when the light travels from B to C, Since nc < nB and v=(c/n), the speed of the light ray will increase in the second medium (C).
Q. No. 20) (i) Explain why the refractive index of any material with respect to air is always greater 1.
(ii) In the figure below a light ray travels from the air into the semi-circular plastic block. Give a reason why the ray does not deviate at the semi-circular boundary of the plastic block.
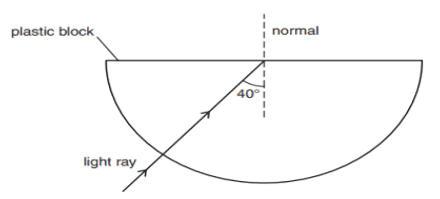
(iii) Complete the ray diagram of the above scenario when the light ray comes out of the plastic block from the top flat end.
Ans. (i) The refractive index of a medium with respect to air is given by Speed of light in air/Speed of light in the medium. Since the speed of light in the medium is always less than the speed of light in air, hence the above ratio is always greater than 1.
ii. The ray of light is undergoing normal incidence at the air-plastic block interface. And for normal incidence, there is no deviation.
iii.
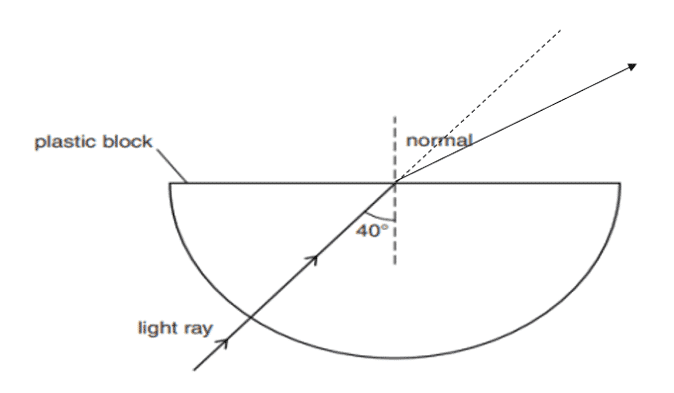
Q. No. 21) Refractive index of diamond with respect to glass is 1.6 and the absolute refractive index of glass is 1.5. Find out the absolute refractive index of the diamond.
Ans. Refractive index of diamond with respect to glass (ndg) = Absolute refractive index of diamond (nd)/Absolute refractive index of glass (ng)
⇒ 1.6 = nd/1.5
⇒ nd = 1.6 x 1.5 = 2.4
Q. No. 22) A ray of light enters benzene from the air. If the refractive index of benzene is 1.50, by what percent does the speed of light reduce on entering the benzene?
Ans.
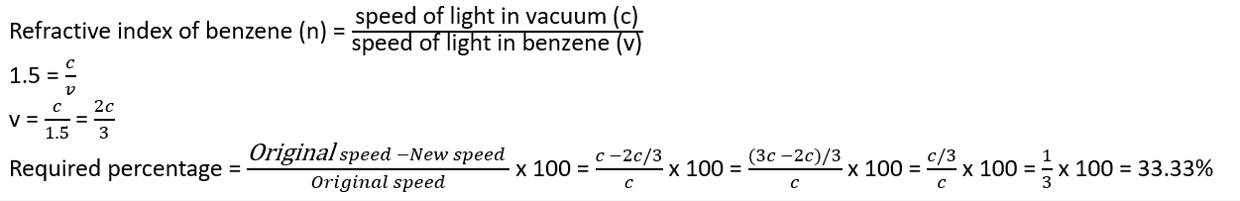
Q. No. 23) i. Name the part of a lens through which a ray of light passes without suffering any deviation.
ii. A girl was playing with a thin beam of light from a laser torch by directing it from different directions on a convex lens held vertically. She was surprised to see that in a particular direction, the beam of light continues to move along the same direction after passing through the lens. State the reason for her observation. Draw a ray diagram to support your answer.
Ans. i. Optical center.
ii.
The girl must have directed the ray of light along the direction of the optical center of the lens because the ray of light passes straight through the optical center of the lens.
Q. No. 24) Can a convergent lens in one medium become divergent in another medium?
Ans. Yes, when the refractive index of the medium is greater than the refractive index of the material of the lens.
Q. No. 25) An object is placed 80 cm from a converging lens of focal length 25 cm. What is the nature of the image?
Ans.
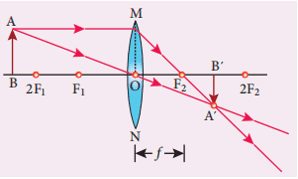
The image is real, inverted, and diminished as the object is placed beyond 2F.
Q. No. 26) A lens produces a magnification of -0.5. Is this a converging or diverging lens? If the focal length of the lens is 6 cm, draw a ray diagram showing the image formation in this case.
Ans. The image will be real and inverted since the magnification has a negative value. The lens that can produce a real and inverted image is a converging lens (convex lens).

Q. No. 27) i. One half of a convex lens of focal length 10 cm is covered with black paper. Can such a lens produce an image of a complete object placed at a distance of 30 cm from the lens? Draw a ray diagram to justify your answer.
ii. A 5 cm tall object is placed on the principal axis of a convex lens of focal length 50 cm at a distance of 40 cm from it. Find the nature, position, and size of the image.
Ans. i. Yes, the lens will produce a complete image of the object but the brightness/intensity of the image will be less.
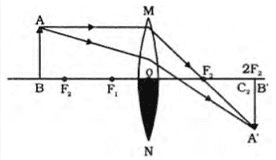
ii.

Q. No. 28) Rohit focused the image of a candle flame on a white screen using a convex lens. He noted down the position of the candle, screen, and lens as under:
Position of candle = 26.0 cm
Position of convex lens = 50.0 cm
Position of screen = 74.0 cm
i. What is the focal length of the convex lens?
ii. Where will the image be formed if he shifts the candle towards the lens at a position of 38 cm?
iii. Draw a ray diagram to show the formation of the image in case (ii) as said above?
Ans. i. u = 50 - 26 = 24 cm
v = 74 - 50 = 24 cm
Since, u = v, therefore object is placed at 2F
⇒ 2f = 24
⇒ f = 12 cm.
ii. u'= 50-38 = 12 cm
i.e., the object (candle) is at focus ⇒ the image will be formed at infinity.
iii.
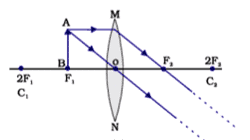
Q. No. 29)
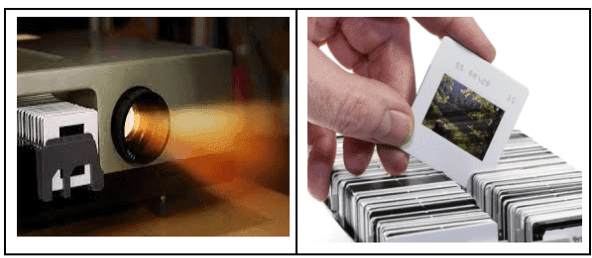
The above images are that of a specialized slide projector. Slides are small transparencies mounted in sturdy frames ideally suited to magnification and projection since they have a very high resolution and a high image quality. There is a tray where the slides are to be put into a particular orientation so that the viewers can see the enlarged erect images of the transparent slides. This means that the slides will have to be inserted upside down in the projector tray.
To show her students the images of insects that she investigated in the lab, Mrs. Iyer brought a slide projector. Her slide projector produced a 500 times enlarged and inverted image of a slide on a screen 10 m away.
a. Based on the text and data given in the above paragraph, what kind of lens must the slide projector have?
b. If v is the symbol used for image distance and u for object distance then with one reason state what will be the sign for v/u in the given case.
c. A slide projector has a convex lens with a focal length of 20 cm. The slide is placed upside down 21 cm from the lens. How far away should the screen be placed from the slide projector’s lens so that the slide is in focus?
d. When a slide is placed 15 cm behind the lens in the projector, an image is formed 3 m in front of the lens. If the focal length of the lens is 14 cm, draw a ray diagram to show image formation.
Ans. a. Since the image formed is enlarged and inverted means the lens is a convex lens.
b. u is always negative, v is positive in this case (imagine from ray diagram)
Therefore, v/u is negative.
Or,
Since the image is inverted, means m = v/u will be negative.
c. f = 20 cm, u = -21 cm, v = ?
By lens formula,
1/f = 1/v - 1/u
⇒ 1/20 = 1/v + 1/21
⇒ 1/v = 1/20 - 1/21 = 1/420
⇒ v = 420 cm
d.
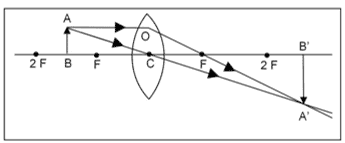
Q. No. 30) A lens forms a blurred image of an object on the screen as shown below:
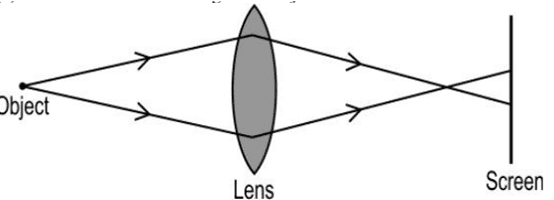
What changes can you make to the following to form a sharp and in-focus image on the screen?
i. Object distance
ii. Focal length of the lens.
Ans. i. Decrease the object distance.
ii. Increase the focal length.
Q. No. 31) If the image formed by a lens formed for all positions of an object placed in front of it is always erect and diminished, what is the nature of this lens? Draw a ray diagram to justify your answer.
Ans. This is a concave lens.
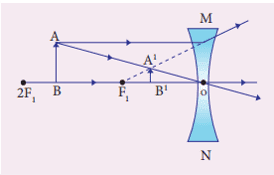
Q. No. 32) Find the position of the object of height 5 cm in front of a concave lens of focal length 20 cm to get the image at a distance of 15 cm from the lens. Also, find the height and nature of the image formed.
Ans.
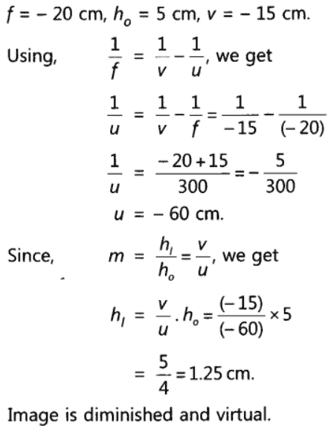
Q. No. 33) A student focused the image of a candle flame on a white screen using a convex lens. He noted down the position of the candle screen and the lens as under.
Position of candle = 12 cm
Position of convex lens = 50 cm
Position of the screen = 88 cm
i. What is the focal length of the convex lens?
ii. Where will the image be formed if he shifts the candle towards the lens at a position of 31 cm?
iii. What will be the nature of the image formed if he further shifts the candle towards the lens?
iv. Draw a ray diagram to show the formation of the image in case (iii) as said above.
Ans. i. u = 50 – 12 = (-) 38 cm [Negative because u is always taken as negative]
v = 88-50 = 38 cm
Since, u = v, therefore the object is placed at 2F
⇒ 2f = 38
⇒ f = 19 cm.
ii. u’= 50-31 = -19 cm
Since the object is placed at focus, therefore the image will be formed at infinity.
iii. If the object is placed within focus, the image formed will be virtual, erect, and magnified.
iv.

Q. No. 34) Define the power of a lens. What is its unit? One student uses a lens of a focal length of 50 cm and another of -50 cm. What is the nature of the lens and its power used by each of them?
Ans. The power of a lens is defined as the reciprocal of its focal length.
P = 1/f (in m) = 100/f (in cm)
Unit of power is dioptre (D).
The lens is convex in the first case and concave in the second case.
P1 = 100/50= 2 D
P2 = 100/(-50)= - 2 D
Q. No. 35) Define one dioptre of power of a lens. You have three lenses L1, L2, and L3 of powers +10D, +5D, and -10D respectively. State the nature and focal length of each lens. Explain which of the three lenses will form a virtual and magnified image of an object placed 15 cm from the lens. Draw the ray diagram in support of your answer.
Ans. Power of a lens is 1 D if the focal length of the lens is 1 m.
For L1: f1 = 100/10 = 10 cm (convex lens)
For L2: f2 = 100/5 = 20 cm (convex lens)
For L3: f3 = 100/(-10) = -10 cm (concave lens)
Lens L2 will form a virtual and magnified image because its focal length is 20 cm and the object is placed at 15 cm i.e., with the focus of the lens.

Hope these questions were helpful to you in preparing for your exams. Please share this with your friends and do comment if you have any doubts/suggestions to share.
Sir kya apne CBSE ka practice papers check kiye ? Sir please do it and make a video on that and specially maths standard.
Haa standard maths ka official sample paper solution already uploaded hai channel pe
Sir wo nhi ek aur aaya hai practice paper 📃
Kaunsa practice paper? CBSE ne toh officially sirf sample papers release kiya hai for 2022-23
Sir ye wale practice paper.
https://cbseacademic.nic.in//additionalPQ.html
Okay. Isme se maximum questions mere important questions se solve ho jayenge. Aur baaki jo naye questions hai, hum unko important questions me update kar denge.
Abhi hum ispe video toh nahi bana sakte kyuki abhi setup Ka issues hai. Tum ek baar ye questions khud try karo aur agar koi question me doubt hota hai toh mereko Instagram me message karo.
Sir plz nationalism in India ka extra questions dijiye
Haa next iss pe hi upload karenge.
Sir if read this question which u sent for board exam can we get good marks
Most probably. It depends on how well you prepare these questions and understand the concepts behind the questions.
Sir 13 MCQ Mae doubt hae
alcohol/flint hona tha
Plz sir reply fast
Nahi agar velocity hota toh alcohol/flint hota. Yaha par RI hai. Isiliye flint/alcohol hoga.
Ok sir
Thanks…
Excellent materials in science subjects also. I hope sir for coming class 11 you will also make your excellent notes for Physics, Chemistry, English and Math also.
Glad you liked it
sir how 0 degrees is the angle of incidence in first question
At point O, the angle between normal and incident ray is 0 degree
Sir can you launch a series full of competency(hard) questions, as in our pre board we will get competative exam papers?
Sir can you launch a series full of competency(hard) questions, as in our pre board we will get competative exam papers?
sir download nhi hota hai pdf
How to Download PDF from CBSE Guidance Website
https://youtu.be/zjocgf0LzUM
thank you for the amazing questions.. i have just found this site after my preboards and ive realised most of the questions are asked from here.. my luck. amazing website!