Is Matter Around Us Pure? Chapter 2 Class 9 Science Important Questions
In this article you will get all the important questions from the chapter- Is Matter Around Us Pure? Class 9 Science. Students must prepare these questions compiled by CBSE Guidance to score maximum in their exam.
1. An element is sonorous and highly ductile. Under which category would you classify this element? What other characteristics do you expect the element to possess?
Ans. The element is a metal. Other Characteristics: Malleable, ductile, good conductor of heat and electricity, shiny, etc.
2. Name two mixtures that can be separated using distillation.
Ans. Alcohol and water, Acetone and water.
3. Which of the following are homogeneous in nature?
i. Ice ii. Wood iii. Soil iv. Air
Ans. Ice and air
4. Name two metalloids.
Ans. i. Silicon ii. Germanium
5. List any two uses of chromatography.
Ans. To separate:
i. Colours of a dye
ii. Pigments from natural colors
iii. Drugs from blood
6. When do we use the method of fractional distillation?
Ans. We use this method to separate two or more miscible liquids for which the difference in boiling points is less than 25 K.
7. State the principle used in centrifugation? List any two uses of centrifugation.
Ans. The principle of centrifugation is that the denser particles are forced to settle at the bottom while the lighter particles stay at the top when spun rapidly.
Applications:
i. Used in dairy to separate butter from cream
ii. Used for blood and urine test
iii. Used in a washing machine to squeeze out water from clothes.
8. Define a solute and a solvent.
Ans. Solute: The component of the solution that is dissolved in the solvent (usually present in a lesser quantity) is solute.
Solvent: The component of a solution that dissolves the other component in it (usually the component present in a larger amount) is called the solvent.
9. Give some examples of the Tyndall effect observed in your surroundings?
Ans. Tyndall effect can be seen when light passes through a heterogeneous mixture.
Example:
i. When a fine beam of light enters a room through a small hole.
ii. When sunlight passes through the canopy of a dense forest.
10. What is the Tyndall effect? Why does the solution of sodium chloride not show the Tyndall effect whereas the mixture of water and milk shows it?
Ans. The scattering of light by colloidal particles is called the Tyndall effect. A salt solution does not show the Tyndall effect because the particles of salt solution are extremely small in size, so such small particles cannot scatter light rays falling on them. Whereas milk solution particles are bigger enough to scatter the light passing through it.
11. Give an example of a solid and a gaseous solution.
Ans. Solid solution: Alloys, Gaseous solution: Air
12. What is an alloy? Give an example.
Ans. Alloys are mixtures of two or more metals or a metal and a non-metal and cannot be separated into their components by physical methods.
Example: Brass is a mixture of approximately 30% zinc and 70% copper.
13. A mixture of Sulphur and carbon disulphide is
a. Heterogeneous and shows the Tyndall effect
b. Homogenous and shows Tyndall effect
c. Heterogenous and does not show Tyndall effect
d. Homogeneous and does not show the Tyndall effect
Ans. Homogeneous and does not show the Tyndall effect.
14. A group of students took an old shoe box and covered it with black paper from all sides. They fixed a source of light (a torch) at one end of the box by making a hole in it and made another hole on the other side to view the sample taken in a beaker/glass tumbler as shown in the figure. They were amazed to see that milk taken in the glass was illuminated. They tried the same activity by taking a salt solution but found that light simply passed through it.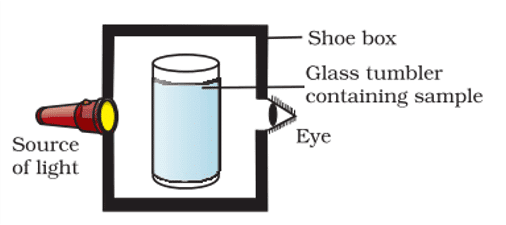
a. Explain why the milk sample was illuminated. Name the phenomenon involved.
b. Same results were not observed with a salt solution. Explain.
c. Can you suggest two more solutions that would show the same effect as shown by the milk solution?
Ans. a. Milk is a colloid and would show the Tyndall effect.
b. Salt solution is a true solution and would not scatter light.
c. Detergent solution, Sulphur solution.
15. Fill in the blanks:
a. A colloid is a ________ mixture and its components can be separated by the technique known as _________.
b. Ice, water, and water vapor look different and display different _____ properties but they are ______ the same.
c. A mixture of chloroform and water are taken in a separating funnel is mixed and left undisturbed for some time. The upper layer in the separating funnel will be of _____ and the lower layer will be that of _____.
d. A mixture of two or more miscible liquids, for which the difference in the boiling points is less than 25 K can be separated by the process called ______.
e. When light is passed through water containing a few drops of milk, it shows a bluish tinge. This is due to the _____ of light and the phenomenon is called ______. This indicates that milk is a ______ solution.
f. Tincture of iodine has antiseptic properties. This solution is made by dissolving _____________
Ans. a. heterogenous, centrifugation
b. Physical, chemically
c. Water, chloroform (density of water is less than that of chloroform)
d. Fractional distillation
e. Scattering, Tyndall effect, colloidal
f. Iodine in alcohol.
16. During an experiment the students were asked to prepare a 10% solution of sugar in water. Ramesh dissolved 10g of sugar in 100g of water while Sarika prepared it by dissolving 10g of sugar in water to make 100g of the solution.
a. Are the two solutions of the same concentration?
b. Compare the mass % of the two solutions.
Ans. a. No,
b. Mass % = (Mass of solute )/(Mass of solute + Mass of solvent ) x 100
The solution made by Ramesh
Mass % = 10/(10+100) x 100 = 10/110 x 100 = 9.09%
The solution made by Sarika
Mass % = 10/100 x 100 = 10 %
17. Calculate the mass of sodium sulphate required to prepare its 20 % (mass percent) solution in 100g of water?
Ans. Let the mass of sodium sulphate required = x g
The mass of solution = (x+100) g
Mass % = 20%
Mass % = (Mass of solute )/(Mass of solute + Mass of solvent ) x 100
20 = x/(x+100) x 100
20x + 2000 = 100x
80x = 2000
X= 2000/80 = 25 g
18. Explain why particles of a colloidal solution do not settle down when left undisturbed, while in the case of a suspension they do.
Ans. Particle size in a suspension is larger than those in a colloidal solution. Also, molecular interaction in a suspension is not strong enough to keep the particles suspended and hence they settle down.
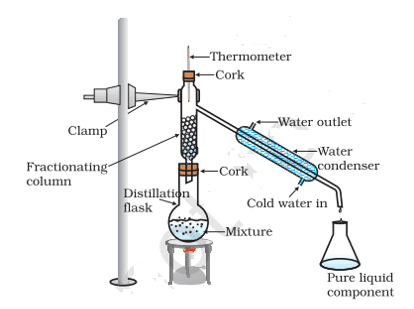
19. Fractional distillation is suitable for the separation of miscible liquids with a boiling point difference of about 25 K or less. What part of the fractional distillation apparatus makes it efficient and possesses an advantage over a simple distillation process? Explain using a diagram.
Ans. The fractionating column packed with glass beads provides a surface for the vapors to collide and lose energy so that they can be quickly condensed and distilled. Also, the length of the column would increase efficiency.
20. Name the method used to separate the components of air. Draw a flow chart to explain the same.
Ans. Fractional distillation
Air
|
Compress and cool by increasing pressure and decreasing temperature
|
Liquid Air
|
Allow to warm up slowly in the fractional distillation column
|
Gasses get separated at different heights
|
| Oxygen | Argon | Nitrogen | |
| Boiling Point (°C) | -183 | -186 | -196 |
| % Air by Volume | 20.9 | 0.9 | 78.1 |
21. Write four differences between Mixtures and compounds.
Ans.
| Mixtures | Compounds |
| 1. Elements or compounds just mix together to form a mixture and no new compound is formed. | 1. Elements react to form new compounds. |
| 2. A mixture has a variable composition. | 2. The composition of each new substance is always fixed. |
| 3. A mixture shows the properties of the constituent substances. | 3. The new substance has totally different properties. |
| 4. The constituents can be separated fairly easily by physical methods. | 4. The constituents can be separated only by chemical or electrochemical reactions. |
| Also Read: |
Watch the Detailed Explanation of this Chapter Here: