Embrace chemistry mastery with our comprehensive collection of key questions and answers for Metals and Non-metals, Chapter 3 of Class 10 Chemistry. This meticulously crafted resource encompasses all the essential concepts and topics covered in the chapter, ensuring you are well-equipped to tackle any question that may arise.
In addition to the textbook questions, we have included extra questions to challenge your understanding and prepare you for the upcoming CBSE 2024-25 board exams. To further enhance your learning experience, we have compiled a downloadable PDF version of the questions and answers, allowing you to study anytime, anywhere.
Embrace simplified chemistry and propel your exam preparation to new heights with our Metals and Non-metals Class 10 Important Questions and Answers.

| Subject | Science (Chemistry) |
| Class | 10 |
| Board | CBSE & State Boards |
| Chapter No. | 3 |
| Chapter Name | Metals and Non-metals |
| Type | Important Questions Answers |
| Session | 2024-25 |
"The difference between ordinary and extraordinary is that little extra."
- Jimmy Johnson
Metals and Non-Metals Class 10: Important Questions & Answers
Q. No. 1) Multiple Choice Questions (MCQs)
i. Which of the following are correctly matched?
| 1. Ductility | Drawn into wire |
| 2. Malleability | Drawn into sheets |
| 3. Good conductors of heat | Copper and mercury |
| 4. Non-metals | Solids or gases |
a. 1, 2 and 3
b. 1, 2 and 4
c. 1, 3 and 4
d. 2, 3 and 4
Ans. Option (b)
ii. Aluminium is used for making cooking utensils. Which of the following properties of aluminium are responsible for the same?
- Good thermal conductivity
- Good electrical conductivity
- Ductility
- High melting point
a. I and II
b. I and III
c. II and III
d. I and IV
Ans. Option (d)
iii. Shown below is a container that is used in the transportation of goods over long distances.

These containers are made of steel. Which property of steel is mainly used to make these containers?
a. Its ductility
b. Its malleability
c. Its metallic lustre
d. Its electrical conductivity
Ans. Option (b)
iv. A cable manufacturing unit tested a few elements on the basis of their physical properties.
| Properties | W | X | Y | Z |
| Malleable | Yes | No | No | Yes |
| Ductile | Yes | No | No | Yes |
| Electrical Conductivity | Yes | Yes | Yes | No |
| Melting Point | High | Low | Low | High |
Which of the above elements were discarded for usage by the company?
a. W, X, Y
b. X, Y, Z
c. W, X, Z
d. W, X, Z
Ans. Option (b)
v. Match the items in column I with the items in column II.
| Column I | Column II |
| 1. Iron | A. Liquid at room temperature |
| 2. Copper | B. Deposition of reddish-brown layer on exposure to moist air |
| 3. Potassium | C. Can be cut easily with a knife |
| 4. Mercury | D. Formation of a greenish layer on exposure to moist air |
Select the correct alternative.
a. 1-A, 2-C, 3-D, 4-B
b. 1-B, 2-D, 3-C, 4-A
c. 1-C, 2-A, 3-B, 4-D
d. 1-D, 2-B, 3-A, 4-C
Ans. Option (b)
vi. Which of the following are correctly matched?
| 1. Mercury | liquid at room temperature |
| 2. Iodine | non-lustrous |
| 3. Lithium | low melting point |
| 4. Graphite | good conductor |
a. 1, 2 and 3
b. 1, 2 and 4
c. 1, 3 and 4
d. 2, 3 and 4
Ans. Option (c)
vii. Although metals form basic oxides, which of the following metals forms an amphoteric oxide?
a. Na
b. Ca
c. Al
d. Cu
Ans. Option (c) [Such metal oxides which react with both acids, as well as bases to produce salts and water, are known as amphoteric oxides. Aluminium oxide reacts in the following manner with acids and bases]
viii. An element with atomic number_____ will form a basic oxide.
a) 7 (2,5)
b) 17 (2,8,7)
c) 14 (2,8,4)
d) 11 (2,8,1)
Ans. Option (d)
ix. Fill in the blank:
In the given reaction, Al2O3 + NaOH → _____ + H2O
a. NaAlO2
b. Na3Al
c. Na2O3
d. NaAl2O3
Ans. Option (a)
x. Which one of the following metals does not react with cold as well as hot water?
a. Na
b. Ca
c. Mg
d. Fe
Ans. Option (d) [Metals like aluminium, iron, and zinc do not react either with cold or hot water. But they react with steam to form metal oxide and hydrogen.]
xi. Which of the following oxide(s) of iron would be obtained on the prolonged reaction of iron with steam?
a. FeO
b. Fe2O3
c. Fe3O4
d. Fe2O3 and Fe3O4
Ans. Option (c) [3Fe (s)+ 4H2O (g) → Fe3O4 (s) + 4H2 (g)]
xii. What happens when calcium is treated with water?
- It does not react with water
- It reacts violently with water
- It reacts less violently with water
- Bubbles of hydrogen gas formed stick to the surface of the calcium
Options
a. I and IV
b. II and III
c. I and II
d. III and IV
Ans. Option (d) [Ca (s) + 2H2O (l) → Ca(OH)2 (aq) + H2 (g)]
xiii. Generally metals react with acids to give salt and hydrogen gas. Which of the following acids does not give hydrogen gas on reacting with metals (except Mn and Mg)?
a. H2SO4
b. HCl
c. HNO3
d. All of these
Ans. Option (c)
xiv. When brass, an alloy of Zn and Cu, is dissolved in dil. HCl, hydrogen gas is evolved. The evolution of gas is due to:
a. Only copper reacts with dil. HCl
b. Only zinc reacts with dil. HCl
c. Both zinc and copper react with dil. HCl
d. Zinc reacts with copper
Ans. Option (b) [In metal reactivity series, Zn is above H and Cu is below H]
xv. A piece of zinc (Zn) – a reactive metal – was dropped into a test tube containing a substance. A zinc salt was formed and hydrogen gas was liberated. This is shown in the equation below.
Zn + _____ → zinc salt + H2 gas
Which of the following can be the substance that zinc was dropped into?
- Water
- Hydrochloric acid
- A solution of zinc salt
Options
a. Only I
b. Only II
c. Only III
d. Either I or III
Ans. Option (b) [Note: copper does not react with dilute HCl]
xvi. The diagram shows the reaction between metal and dil. Acid.
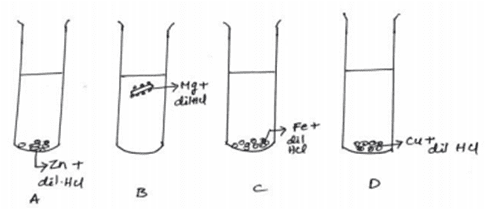
What is the reason for the different behavior of Mg in test tube B?
a. Mg is a lighter element than dil. HCl
b. Mg reacts with dil. HCl to produce H2 gas which helps in floating
c. Mg reacts with dil. HCl to produce N2 gas which helps in floating
d. Mg reacts with dil. HCl to produce CO2 gas which helps in floating
Ans. Option (b)
xvii. The metal X does not react with cold water but floats on hot water with the formation of colorless bubbles. Which of the following represents metal X.
a) Aluminium
b) Copper
c) Magnesium
d) Lead
Ans. Option (c)
xviii. On placing a copper coin in a test tube containing green ferrous sulphate solution, it will be observed that the ferrous sulphate solution
a. Turns blue, and a grey substance is deposited on the copper coin.
b. Turns colorless and a grey substance is deposited on the copper coin.
c. Turns colorless and a reddish-brown substance is deposited on the copper coin.
d. Remains green with no change in the copper coin.
Ans. Option (d) [Cu is below Fe in the reactivity series]
xix. The colour of the solution observed after 30 minutes of placing zinc metal to copper sulphate solution is
a) Blue
b) Colourless
c) Dirty green
d) Reddish Brown
Ans. Option (b)
xx. On adding dilute sulphuric acid to a test tube containing a metal ‘X’, a colourless gas is produced when a burning match stick is brought near it. Which of the following correctly represents metal ‘X’?
a) Sodium
b) Sulphur
c) Copper
d) Silver
Ans. Option (a)
xxi. An element ‘M' has 50% of the electrons filled in the 3rd shell as in the 2nd shell. The atomic number of ‘M’ is:
a) 10
b) 12
c) 14
d) 18
Ans. Option (c)
xxii. Which one of the following correctly represents Sodium oxide?
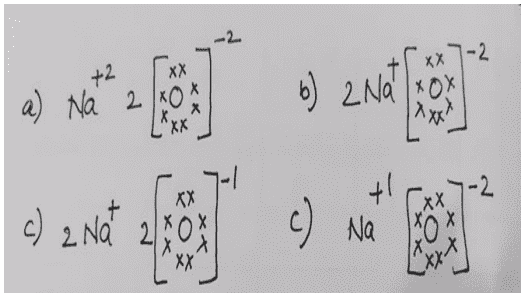
Ans. Option (b)
xxiii. Sodium comes after potassium in the reactivity series, so sodium is _____.
a. Not reactive
b. More reactive than potassium
c. Equally reactive as potassium
d. Less reactive than potassium
Ans. Option (d)
xxiv. Given below are reactions involving metals P, Q, R, and S and their salt solutions in water.
- Metal P salt solution + Q → Metal Q salt solution + P
- Metal Q salt solution + R → Metal R salt solution + Q
- Metal S salt solution + Q → Metal Q salt solution + S
- Metal P salt solution + S → No reaction
Which metal is the MOST reactive?
a. P
b. Q
c. R
d. S
Ans. Option (c)
xxv. The electronic configurations of three elements X, Y, and Z are
X – 2, 8; Y – 2, 8, 7 and Z – 2, 8, 2.
Which of the following is correct?
a. X is a metal
b. Y is a metal
c. Z is a non-metal
d. Y is a non-metal and Z is a metal
Ans. Option (d)
xxvi. Which of the following are not ionic compounds?
- KCl
- HCl
- CCl4
- NaCl
Options
a. I and II
b. II and III
c. III and IV
d. I and III
Ans. Option (b)
xxvii. The electronic structures of six elements A to F are given in the table below:
| Electronic Structure | Formula of Compound | ||
| 1. | A: 2, 1 | B: 2, 6 | A2B |
| 2. | B: 2, 6 | C: 2, 7 | B2C |
| 3. | C: 2, 7 | D: 2, 8, 3 | DC3 |
| 4. | E: 2, 8, 6 | F: 2, 8, 8, 2 | FE2 |
Which of the compounds formed are wrong?
a. 1 and 3
b. 2 and 3
c. 3 and 4
d. 2 and 4
Ans. Option (b)
xxviii. A scientist is attempting to represent an ionic bond between calcium and chlorine. The figure below shows the progress he has made so far.
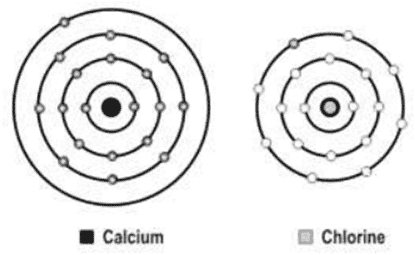
What should be the next step in his representative of the ionic bond?
a. Transfer an electron from the calcium atom to the chlorine atom.
b. Transfer an electron from the chlorine atom to the calcium atom.
c. Add another chlorine atom to accept an electron from the calcium atom.
d. Add another calcium atom to donate an electron to the chlorine atom.
Ans. Option (c)
xxix. In which of the following forms do electrovalent compounds conduct electricity?
a. Only in solid form
b. Both in solid form and in aqueous solution
c. Both in aqueous solution and in molten form
d. In solid form, molten form, and in aqueous solution
Ans. Option (c)
xxx. The table shown below gives information about four substances: A, B, C, and D.
| Substance | Melting Point (K) | Electrical Conductivity | |
| Solid | Liquid/Aqueous | ||
| A | 295 | Good | Good |
| B | 1210 | Poor | Good |
| C | 1890 | Poor | Good |
| D | 1160 | Poor | Poor |
Identify ionic compounds from the above-given substances.
a. A, B
b. B, C
c. A, B, D
d. A, C, D
Ans. Option (b)
xxxi. Listed here is the reactivity of certain metals.
| Metal | Reaction with air | Reaction with water | Reaction with dilute acids |
| Gold | Does not oxidize or burn | No reaction | No reaction |
| Sodium | Burns vigorously to form oxide | Violent reaction | Violent reaction |
| Zinc | Burns to form oxides | Reacts on heating with water | Reacts to produce hydrogen |
| Platinum | Does not oxidize or burn | No reaction | No reaction |
Which of the above metals are likely to be obtained in their pure states from the Earth’s crust?
a. Gold only
b. Sodium only
c. Gold and platinum
d. Zinc and sodium
Ans. Option (c)
xxxii. Metals are refined by using different methods. Which of the following metals are refined by electrolytic refining?
- Au
- Cu
- Na
- K
Options
a. I and II
b. I and III
c. II and III
d. III and IV
Ans. Option (a) [Metals such as copper, zinc, tin, nickel, silver, gold, etc., are refined electrolytically]
xxxiii. Ashok has written the following reactions to show how metals can be obtained from their ores.
- 2Fe2O3 + 3C → 4Fe + 3CO2
- Na2O + C → 2Na + CO
- ZnO + C → Zn + CO
- CuO + C → Cu + CO
Identify the INCORRECT reaction(s) among them.
a. Only I
b. Only II
c. Only I and III
d. Only II, III, and IV
Ans. Option (b)
xxxiv. During the electrolytic refining of copper what happens at the anode?
a. Copper ions gain electrons to become neutral copper atoms
b. Neutral copper atoms gain electrons to become ions
c. Copper ions lose electrons to become neutral atoms
d. Neutral copper atoms lose electrons to become ions
Ans. Option (d)
xxxv. During the purification of a metal by electrolysis, what happens at the negative electrode?
(a) Metal ions lose electrons to become neutral atoms.
(b) Neutral metal atoms gain electrons to become ions.
(c) Neutral metal atoms lose electrons to become ions.
(d) Metal ions gain electrons to become neutral metal atoms.
Ans. Option (d)
xxxvi. If copper is kept open in the air, it slowly loses its shining brown surface and gains a green coating. It is due to the formation of
a. CuSO4
b. CuCO3
c. Cu(NO3)2
d. CuO
Ans. Option (b)
xxxvii. Assertion Reason Based Question:
- Assertion: Rusting of Iron is endothermic in nature.
- Reason: As the reaction is slow, the release of heat is barely evident.
a) Both A and R are true, and R is the correct explanation of A.
b) Both A and R are true, and R is not the correct explanation of A.
c) A is true but R is false.
d) A is false but R is true.
Ans. Option (d)
xxxviii. Alloys are homogeneous mixtures of a metal with a metal or non-metal. Which among the following alloys contain non-metal as one of its constituents?
a. Brass
b. Bronze
c. Amalgam
d. Steel
Ans. Option (d)
[Amalgum: If one of the metals is mercury, then the alloy is known as an amalgam.
Brass: An alloy of copper and zinc (Cu and Zn)
Bronze: An alloy of copper and tin (Cu and Sn)
Solder: An alloy of lead and tin (Pb and Sn)
Stainless steel: Iron is mixed with nickel and chromium (Ni and Cr)]
xxxix. 2 mL each of concentrated HCl, HNO3, and a mixture of concentrated HCl and concentrated HNO3 in the ratio of 3:1 were taken in test tubes labeled as A, B, and C. A small piece of metal was put in each test tube. No change occurred in test tubes A and B but the metal got dissolved in test tube C respectively. The metal could be
a. Al
b. Au
c. Cu
d. Pt
Ans. Option (b) [Aqua regia is a freshly prepared mixture of concentrated hydrochloric acid and concentrated nitric acid in the ratio of 3:1. It can dissolve gold, even though neither of these acids can do so alone.]
XL. Galvanisation is a process of coating iron articles with a layer of zinc to prevent the iron from rusting.
The iron is protected even if the zinc coating is scratched and the iron is exposed.
Which of the following is true about how zinc prevents the rusting of iron?
- A galvanized iron article does not undergo oxidation.
- The zinc coating prevents contact of iron with air.
- Zinc undergoes corrosion more easily than iron.
(a) only 1
(b) only 2
(c) only 1 and 2
(d) only 2 and 3
Ans. Option (d)
Q. No. 2) Distinguish between the physical properties of metals and non-metals in a tabular form.
Ans.
| Property | Metals | Non-metals |
| 1. Lustre | Metals have shining surfaces. | They do not have shining surfaces.
|
| 2. Hardness | They are generally hard.
| Generally soft.
|
| 3. State | Exist as solids.
| Exist as solids or gases.
|
| 4. Malleability | Metals can be beaten into thin sheets.
| Non-metals are non-malleable. |
| 5. Ductility | Metals can be drawn into thin wires. | They are non-ductile. |
| 6. Conductor of heat and electricity | Metals are good conductors of heat and electricity.
| Non-metals are poor conductors of heat and electricity.
|
| 7. Density | Generally have high density and high melting points.
| Have low density and low melting point. |
| 8. Sonorous | Metals produce a sound on striking a hard surface. | They are not sonorous. |
Q. No. 3) State three reasons why:
a. Sulphur is a non-metal
b. Magnesium is a metal
Ans. a. Sulphur is a non-metal because:
- Sulphur is a poor conductor of electricity.
- Sulphur is brittle.
- It reacts with oxygen to form Sulphur dioxide which forms an acidic solution in water.
b. Magnesium is a metal because:
- Magnesium is a good conductor of electricity.
- It is malleable and ductile.
- It forms basic oxide when it reacts with oxygen.
Q. No. 4) (a) Write the balanced chemical equation for the reaction that is prevented by storing potassium metal under kerosene.
(b) Identify the type of chemical reaction that is prevented.
Ans. (a) 4 K + O2 → 2 K2O
(b) combination reaction OR oxidation reaction
Q. No. 5) How will you show experimentally that metals are good conductors of heat?
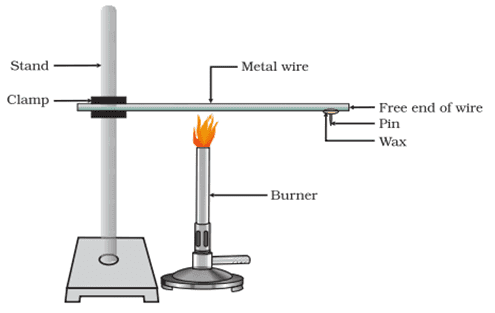
Ans.
Procedure:
- Take an aluminium wire. Clamp this wire on a stand.
- Fix a pin to the free end of the wire using wax.
- Heat the wire with a candle.
Observation: Heat is transferred from the wax and pin falls.
Conclusion: Metals are good conductors of heat.
Q. No. 6) Distinguish between the chemical properties of metals and non-metals in a tabular form.
Ans.
| Property | Metals | Non-metals |
| 1. Nature of ions | Metals are electropositive in nature, so they lose electrons to form positive ions. | Non-metals are electronegative in nature, so they gain electrons to form negative ions. |
| 2. Nature of oxides | Metals form basic or amphoteric oxides. | Non-metals form acidic or neutral oxides. |
| 3. Reaction with water | Metals displace hydrogen from water or steam.
| Non-metals do not displace hydrogen from water or steam. |
| 4. Reaction with dilute acids | Metals that lie above hydrogen in the reactivity series displace hydrogen from dilute acids.
| Non-metals do not react with dilute acids as they do not displace hydrogen from dilute acids. |
Q. No. 7) a. When calcium metal is added to water, the gas evolved does not catch fire but the same gas evolved on adding potassium metal to water catches fire. Explain why?
b. Name a metal for each case:
- It displaces hydrogen gas from nitric acid.
- It does not react with any physical state of water.
- It does not react with cold as well as hot water but reacts with steam.
Ans. a. In both cases, the gas evolved is H2. When calcium reacts with water, the heat evolved is not sufficient for hydrogen to catch fire. On the other hand, potassium reacts with water violently and a lot of heat is evolved which is sufficient for hydrogen to catch fire.
b. 1. Zinc
2. Copper/Lead/Silver/Gold
3. Aluminium/Iron/Zinc.
Q. No. 8) a. What are amphoteric oxides? With the help of chemical equations, explain why Al2O3 is called an amphoteric oxide.
b. Why is it that non-metals do not displace hydrogen from dilute acids?
Ans. a. Amphoteric Oxides: Metal oxides that react with both acids, as well as bases to produce salts and water, are called amphoteric oxides. For example ZnO, Al2O3
Al2O3 + 6HCl → 2AlCl3 + H2O
Al2O3 + 2NaOH → 3NaAlO2 + H2O
b. Non-metals cannot lose electrons to H+ to form H2 gas because non-metals are electron-acceptors hence they do not react with dilute acids.
Q. No. 9) Keerti added dilute Hydrochloric acid to four metals and recorded her observations as shown in the table given below:
| Metal | Gas Evolved |
| Copper | Yes |
| Iron | Yes |
| Magnesium | No |
| Zinc | Yes |
Select the correct observation(s) and give chemical equation(s) of the reaction involved.
Ans. Fe + 2HCl → FeCl2 + H2
Zn + HCl → ZnCl2 + H2
Q. No. 10) Why do metals not evolve hydrogen gas with nitric acid?
Ans. It is because HNO3 is a strong oxidizing agent. It oxidizes the H2 produced to water and itself gets reduced to any of the nitrogen oxides (N2O, NO, NO2 ). But magnesium (Mg) and manganese (Mn) react with very dilute HNO3 to evolve H2 gas.
Q. No. 11) What is reactivity series? How does the reactivity series of metals help in predicting the relative activities of various metals?
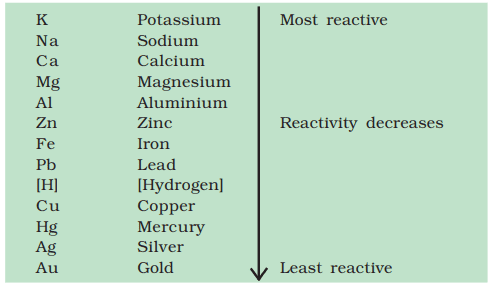
Ans. The reactivity series (also called activity series) is a list of metals arranged in the order of their decreasing activities
A metal placed above hydrogen in the activity series will displace hydrogen from water or acids. A metal placed at the top of the activity series would displace metal below it. Thus a more reactive metal displaces a less reactive metal from its salt solution.
Q. No. 12) Arrange the metals iron, magnesium, zinc, and copper in the increasing order of their reactivity.
What will be the two observations made by the student when iron fillings are added to copper sulphate solution?
Ans. Metals in increasing order of reactivity: Copper, iron, zinc, and magnesium.
Two observations are:
- The color of the solution changes from blue to green.
- Reddish brown deposits on iron fillings.
Q. No. 13) The following observations were made by a student on treating four metals P, Q, R, and S with the given salt solutions:
| Sample | MgSO4 (aq) | Zn(NO3)2 (aq) | CaSO4 (aq) | Na2SO4 (aq) |
| P | No reaction | Reaction occurs | Reaction occurs | No reaction |
| Q | Reaction occurs | Reaction occurs | Reaction occurs | Reaction occurs |
| R | No reaction | Reaction occurs | No reaction | No reaction |
| S | No reaction | No reaction | No reaction | No reaction |
Based on the above observations:
a. Arrange the given samples in the increasing order of reactivity.
b. Write the chemical formulae of products formed when Q reacts with CuSO4 solution.
Ans. a. S > R > P > Q
b. Q + CuSO4 → Cu + QSO4
Q. No. 14) State the reason for the following:
i. An iron strip dipped in a blue copper sulphate solution turns the blue solution pale green.
ii. Calcium does not occur in a free state in nature.
iii. Sodium or potassium metals are kept immersed under kerosene.
iv. Non-metals do not form positively charged ions.
v. Aluminium is a reactive metal but does not corrode easily.
Ans. i. Iron being more reactive than copper displaces copper from copper sulphate to form a green ferrous sulphate solution.
ii. Calcium is a very reactive metal. It reacts with the chemicals in the surroundings and occurs in a combined state.
iii. Sodium and potassium are highly reactive metals and react vigorously with oxygen in the air and may even catch fire. They do not react with kerosene.
iv. Non-metals do not lose electrons to form positive ions. Instead, they gain electrons to form negative ions.
v. Aluminium reacts with oxygen in the air and forms a protective oxide layer and prevents its corrosion.
Q. No. 15) How is Magnesium Chloride formed by the transfer of electrons? Why does the solution of Magnesium Chloride conduct electricity?
Ans. Formation of MgCl2
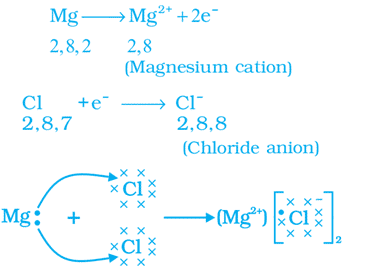
Solution of Magnesium Chloride conducts electricity because an ionic compound dissociates into ions when dissolved in water and hence conducts electricity.
Q. No. 16) Explain the formation of Calcium Chloride with the help of an electron dot structure. (Atomic numbers: Ca=20; Cl=17)
Ans.
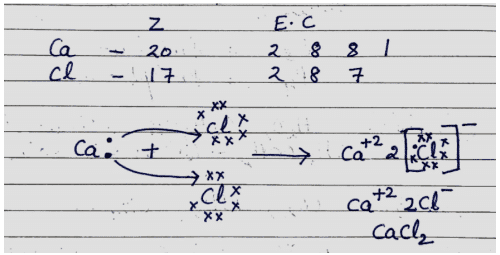
Q. No. 17) An element ‘M’ with electronic configuration 2, 8, 3 combines separately with Cl-, SO4-2 anions. Write the chemical formulae of the compounds formed. Predict with the suitable reason the nature of the bond formed by element ‘M’ in general. How will the electrical conductivity of the compounds formed vary with respect to ‘M’?
Ans. MCl3; M2(SO4)3
M in general forms an Ionic bond. It can acquire a stable electronic configuration of neon (2, 8) by losing its three valence electrons to form M3+cation.
Compounds formed will conduct electricity in liquid / molten state but not in solid state in contrast to ‘M’.
Q. No. 18) What are ionic compounds? Write the properties of ionic compounds.
Ans. Ionic compounds: The compounds formed by the transfer of electrons from a metal to a non-metal are called ionic compounds or electrovalent compounds.
Properties of ionic compounds:
- Physical nature: They are solid and hard, generally brittle.
- Melting and boiling point: They have high melting and boiling point.
- Solubility: Generally soluble in water and insoluble in solvents such as kerosene, petrol, etc.
- Conduction of electricity: Ionic compounds conduct electricity in molten and solution form but not in solid state.
Q. No. 19) Why do ionic compounds not conduct electricity in the solid state but conduct electricity in a molten and aqueous states?
Ans. Ionic compounds in the solid state do not conduct electricity because the movement of ions in the solid is not possible due to their rigid structure. But ionic compounds conduct electricity in the molten state. This is possible in the molten state since the electrostatic forces of attraction between the oppositely charged ions are overcome due to the heat. Thus, the ions move freely and conduct electricity.
Q. No. 20) The electronic configuration of some elements is given in the table below.
| Element | Electronic configuration |
| P | 2, 8, 8 |
| Q | 2, 8, 8, 1 |
| R | 2, 6 |
| S | 2, 5 |
| T | 2, 8, 2 |
| U | 2, 8, 7 |
(a) Identify any two pairs of elements that will react to form compounds by a transfer of electrons.
(b) Write the molecular formula of the compounds formed by the pairs of elements identified in (a).
Ans. a.
- Q and R
- Q and U
- T and R
- T and U
b.
- Q2R
- QU
- TR
- TU2
Q. No. 21) How are ores different than minerals?
Ans.
| Mineral | Ore |
| Natural occurring chemical substances obtained by mining. | An ore is a mineral from which metal is obtained. |
Q. No. 22) A metal X is obtained from its chloride salt by exposure to sunlight.
(a) In which section of the reactivity series of metals- top, middle or bottom, is it likely to be placed? Justify your answer.
(b) Identify the type of reaction the chloride salt of metal X undergoes on exposure to sunlight.
Ans.
(a) bottom section
Metals at the bottom of the reactivity series are the least reactive. They occur in their free state; their compounds are unstable and hence easily converted to metal.
(b) photolytic decomposition
Q. No. 23) Describe the extraction of Mercury metal from its ore Cinnabar (HgS).
Ans. Cinnabar (HgS) is an ore of mercury. When it is heated in air, it is first converted into mercuric oxide (HgO). Mercuric oxide is then reduced to mercury on further heating.
Roasting: 2HgS (s) + 3O2 (g) (Heat) → 2HgO (s) + 2SO2 (g)
Reduction: 2HgO (s) (Heat) → 2Hg (l) + O2 (g)
Q. No. 24) Two ores are heated. Ore A gives CO2, whereas ore B gives SO2. Explain the processes with help of a balanced chemical equation, which is used to convert ores A and B into their oxide ores with an example.
Or,
Write the differences between calcination and roasting.
Ans. Ore A is Carbonate ore. Ore B is Sulphide ore.
| Roasting | Calcination |
| i. Ore is heated in the presence of air. | i. Ore is heated in the absence of air. |
| ii. It converts sulphide ores to oxide ores. | ii. It converts carbonate ores to oxide ores. |
| iii. For example: 2ZnS + 3O2 (heat) → 2ZnO + 2SO2 | iii. For example: FeCO3 (heat) → FeO + CO2 |
Q. No. 25) a. Write the steps involved in the extraction of pure metals in the middle of the activity series from their carbonate ores.
b. In the electrolytic refining of a metal M, what would you take as the anode, the cathode, and the electrolyte?
Ans. a. Extraction of pure metals from Carbonate ores:
i. Concentration of ore: Gangue is removed from the ore.
ii. Calcination: The carbonate ore is heated strongly in absence of air.
ZnCO3 (s) (Heat) → ZnO (s) + CO2 (g)
iii. Reduction by carbon or more reactive metal:
ZnO (s) + C (s) → Zn (s) + CO (g)
b. Electrolytic refining of metal M:
- Anode: Impure metal
- Cathode: Pure metal
- Electrolyte: Acidified Metal Salt solution.
Q. No. 26) a. Why are carbonate or sulphide ores converted to oxides during the process of extraction?
b. Metal X is found in nature as its sulphide XS. It is used in the galvanization of iron articles. Identify the metal X. How will you convert this sulphide ore into the metal? Explain with equations.
Ans. a. Carbonate or sulphide ores are converted to oxides during the process of extraction because it is easier to obtain metal from its oxide, as compared to its sulphides and carbonates.
b. Metal X is Zinc.
The sulphide ore is first heated strongly in supply of oxygen and changed into its oxide. This process is called roasting.
2ZnS (s) + 3O2 (g) (Heat) → 2ZnO (s) + 2SO2 (g)
Zinc oxide is then reduced to zinc metal by heating it with carbon. This process is called reduction.
2ZnO (s) + C (s) (Heat) → 2Zn (s) + CO2 (g)
Q. No. 27) Write chemical equations for the following reactions:
i. Cinnabar is heated in presence of air.
ii. Manganese dioxide is heated with aluminium powder.
Ans. i. 2HgS (s) + 3O2 (g) (Heat) → 2HgO (s) + 2SO2 (g)
2HgO (s) (Heat) → 2Hg (l) + O2 (g)
ii. 3MnO2 (s) + 4Al (s) → 3Mn (l) + 2Al2O3 (s) + Heat
Q. No. 28) Suggest different chemical processes used for obtaining a metal from its oxides for metals in the middle of the reactivity series and metals towards the top of the reactivity series. Support your answer with one example each.
Ans. i. For obtaining metals that are in the middle of the reactivity series, oxides of such metals can be reduced with coke (carbon) which acts as a reducing agent.
For example: 2Fe2O3 + 3C → 4Fe + 3CO2
ii. For obtaining metals that are high in the reactivity series, their oxides are reduced to metals by the process of electrolysis.
For example The electrolysis of sodium chloride
At cathode: Na+ + e- → Na
At anode: 2Cl- → Cl2 + 2e-
Q. No. 29) The Thermit process is used for repairing cracks in railway tracks on site.
a. Write the equation for the reaction taking place in the process, mentioning the physical states of the reactants and products.
b. What information in the chemical equation indicates that the reaction is exothermic?
Ans. a. 2Al (s) + Fe2O3 (s) → 2Fe (l) + Al2O3 (s) [Note: Here writing states is very important]
b. The iron formed is in the molten (liquid) state due to the heat generated in the reaction.
Q. No. 30) a. Identify the reaction given below:
Fe2O3 + 2Al → Al2O3 + 2Fe + Heat
b. Identify the oxidizing and reducing agents in this reaction.
c. State an application of this reaction.
Ans. a. This is a Thermit reaction (displacement reaction).
b. Al is the reducing agent and Fe2O3 is the oxidizing agent.
c. This reaction is highly exothermic and the metals are produced in the molten state in this reaction so this reaction is used to join railway tracks or cracked machine parts.
Q. No. 31) The given reaction shows one of the processes to extract metals like Iron and Manganese.
MnO₂ (s) + Al(s) → Mn(l) + Al₂O₃(s) + Heat
a) Give a reason why the above reaction is known as a thermite reaction.
b) Identify the substance oxidized and reduced in the above reaction.
c) Give a reason why Aluminium is preferably used in thermite reactions.
Ans. a. The above reaction is known as a thermite reaction as
- the reaction is a highly exothermic reaction.
- the metal (Mn/Fe) obtained will be in a molten/ liquid state.
b) Substance oxidized - Al(s)
Substance reduced – MnO2 (s)
c) Aluminium is preferably used in thermite reactions as
- it is placed above Fe and Mn in the reactivity series of metals.
- Al is more reactive than Fe/ Mn
Q. No. 32) Given below are the steps for extraction of copper from its ore.
a. Write the equations of the reactions involved in the roasting of copper (I) suphide followed by its reduction.
b. Draw a neat labeled diagram for electrolytic refining.
Ans. a. 2Cu2S (s) + 3O2 (g) (Heat) → 2Cu2O (s) + 2SO2 (g)
2Cu2O (s) + Cu2S (s) (Heat) → 6Cu (s) + SO2 (g)
b.
Q. No. 33) A reddish-brown metal ‘X’, when heated in air, gives a black compound ‘Y’, which when heated in the presence of H₂ gas gives ‘X’ back. ‘X’ is refined by the process of electrolysis; this refined form of ‘X’ is used in electrical wiring. Identify ‘X’ and ‘Y’.
Ans. ‘X’ - Copper/ Cu and ‘Y’ - CuO.
Q. No. 34) How are metals high in the reactivity series obtained from their ores? Explain the process, by taking an example.
Ans. Metals at the top of the activity series like K, Na, Ca, etc., are very reactive. They cannot be obtained from their compounds by heating with carbon. These metals are obtained by electrolytic reduction. For example, sodium, magnesium, and calcium are obtained by the electrolysis of their molten chlorides. The metals are deposited at the cathode (the negatively charged electrode), whereas, chlorine is liberated at the anode (the positively charged electrode). The reactions are –
At cathode: Na+ + e– → Na
At anode: 2Cl– → Cl2 + 2e–
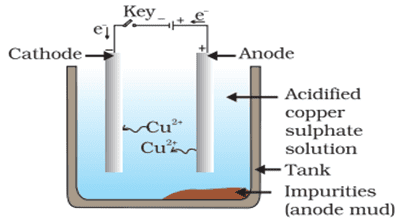
Q. No. 35) What is meant by refining of metals? Name the most widely used method of refining impure metals produced by various reduction processes. Describe with the help of a labeled diagram how this method may be used for refining copper.
Ans. The process of obtaining pure metal from its impure form is called the refining of metals.
The most widely used method for refining impure metals is electrolytic refining.
Electrolytic refining of Copper:

- Anode – Impure copper
- Cathode – Strip of pure copper
- Electrolyte – Solution of acidified copper sulphate
a. On passing the current through the electrolyte, the impure metal from the anode dissolves into the electrolyte.
Cu (Impure copper) → Cu2+ + 2e-
b. An equivalent amount of pure metal from the electrolyte is deposited at the cathode.
Cu 2+ + 2e- → Cu (Pure copper)
c. The insoluble impurities settle down at the bottom of the anode and is called anode mud.
Q. No. 36) a. What is corrosion of iron called?
b. How will you recognize the phenomenon of corrosion of silver?
c. Why corrosion of iron metal is a serious problem?
d. How can we prevent corrosion of iron?
Ans. a. Corrosion of iron is called rusting. Iron when exposed to moist air for a long time acquires a coating of a brown flaky substance called rust.
b. Silver articles become black after some time when exposed to air. This is because it reacts with sulphur in the air to form a coating of silver sulphide.
c. It weakens bridges and materials and a lot of iron gets wasted every year.
d. We can prevent the corrosion of iron by
- Painting
- Oiling and greasing
- Galvanization
- By making alloys.
Q. No. 37) a. What are alloys? Explain, how the properties of alloys are superior to metals by taking three examples.
b. What type of mixture is an alloy?
c. How does the electrical conductivity of an alloy compare with that of pure metal?
Ans. a. Alloy: An alloy is a homogenous mixture of two or more metals or a metal and a non-metal.
Examples:
- Iron: Mixed with a small amount of carbon becomes hard and strong.
- Alloys are made to lower the melting point. Solder, an alloy of lead and tin has a lower melting point, so it is used for joining electrical wires together.
- Alloys are resistant to corrosion. Stainless steel which is made up of iron, chromium, and nickel resists corrosion. It is used for making utensils and surgical instruments.
b. Homogenous.
c. The electrical conductivity of an alloy is less than that of pure metal.
Q. No. 38) Pure gold is very soft and therefore not suitable for making jewellery. To make it hard, gold is alloyed with other metals. The purity of gold is measured in carats according to the table below. Carat number is the number of parts of gold in 24 parts.
| Carat Number | Number of parts of gold in 24 parts | Number of parts of other metals in 24 parts |
| 24 | 24 | 0 |
| 22 | 22 | 2 |
| 18 | 18 | 6 |
| 14 | 14 | 10 |
| 12 | 12 | 12 |
a. What is the percentage of gold in 18-carat gold? Name any two metals that are used to make 22-carat gold.
b. Like gold, pure iron is also comparatively soft and also undergoes rusting. Name the substance that is mixed with iron.
Ans. a. Percentage of gold in 18-carat gold = 18/24 x 100 % = 75 %.
Silver and copper are used to make 22-carat gold.
b. Carbon is mixed with iron to make it hard and strong.
Stainless steel is made up of iron, chromium, and nickel. It resists corrosion.
Q. No. 39) Two students decided to investigate the effect of water and air on the iron objects under identical experimental conditions. They measured the mass of each object before placing it partially immersed in 10 mL of water. After a few days, the object was removed, and dried and their masses were measured. The table shows their results.
| Student | Object | Mass of object before rusting in g | Mass of the coated object in g |
| A | Nail | 3.0 | 3.15 |
| B | Thin plate | 6.0 | 6.33 |
a. What might be the reason for the varied observations of the two students?
b. In another set up the students coated iron nails with zinc metal and noted that iron nails coated with zinc prevent rusting. They also observed that zinc initially acts as a physical barrier, but an extra advantage of using zinc is that it continues to prevent rusting even if the layer of zinc is damaged. Name this process of rust prevention and give any two other methods to prevent rusting.
c. In which of the following applications of iron, rusting will occur most? Support your answer with a valid reason.
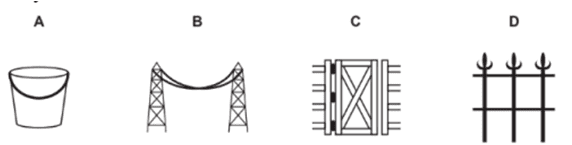
A- Iron bucket electroplated with Zinc
B- Electricity cables having iron wires covered with aluminium
C- Iron hinges on a gate
D- Painted iron fence
Ans. a. Rusting occurs in both A and B so there is an increase in mass. As the surface area of B is the more, the extent of rusting is more.
b. Galvanization.
Methods to prevent rusting:
- Oiling
- Greasing
- Painting
- Alloying
- Chromium plating, etc.
c. C- Iron hinges on a gate. Because iron is in contact with both atmospheric oxygen and moisture/water vapor.
Metals and Non-metals NCERT Underlined PDF
| Must Read: Metals and Non-metals Class 10 Notes |
| You Might Also Like: CBSE Class 10 Notes CBSE Class 10 Important Questions and Answers |
Hope you liked these Important Questions Answers on Class 10 Science Chapter 3 Metals and Non-metals. Please share this with your friends and do comment if you have any doubts/suggestions to share.
Sir iske baad v NCERT Exampler karne hai kya ?
Naa abhi jaruri nahi hai. Time bache toh revision pe focus karo.
Sir question 18 me bohot dought h
Isme p q r s ki reactivity kaise pata chali?
First reaction se pata chala ki: Q>P
Second reaction: R>Q
Therefore R>Q>P
Third reaction: Q>S
Fourth reaction: P>S
Therefore R>Q>P>S
Most reactive is R.
Sir ek doubt h jitna aap question dia h ham sab kar lia h but or kuch bhi padhna h kia 🙏
Pahle ye questions prepare karlo. Fir time bache toh NCERT revision karo.
Compound X and Aluminium are used to join railway tracks (a) identify the compound X (b) name the reaction (c) write down it’s reaction
🫡
Uhr name is so beautiful 🫶🩵
Is tarah ka question board me ayega
Itna padh lenge to ho jaega
Sir apky diye hue revision notes nd yeh imp. questions enough hai boards keh liye??
Sir plz aaap PYQS bhii provide kardo 🙏. It will help us a lot.
Sir XXX¡¡
Iskaa answer d ni aayee ga because highly reactive metals extract hote hai electrically.