Are you studying for your Class 12 Economics exam and need help with Indian Economic Development Chapter 4 Human Capital Formation in India? Look no further! We have compiled a list of important questions and answers to help you prepare and excel in your exam.

| Board | CBSE and State Boards |
| Class | 12 |
| Subject | Economics |
| Book Name | Indian Economic Development |
| Chapter No. | 4 |
| Chapter Name | Human Capital Formation in India |
| Type | Important Questions & Answers |
| Session | 2024-25 |
"Mastering others is strength. Mastering yourself is true power."
- Lao Tzu
human capital formation in India class 12 important questions & answers
Q. No. 1) Multiple Choice Questions (MCQs)
i. Which statement can be said to best describe the importance of expenditure on education?
a. It increases the efficiency and skill of human capital
b. It increases the growth of individuals
c. It decreases earning capacity of individuals
d. It increases the labor charge
Ans. Option (a)
ii. Which of the following is an example of preventive medicine?
a. Medical intervention during illness
b. Spread of health literacy
c. Vaccination
d. Provision of clean drinking water
Ans. Option (c)
iii. Read the following statements carefully.
- Statement 1: On-the-job training help to bridge the gap between theoretical concepts and practical experiences.
- Statement 2: On-the-job training updates the employees, with the latest changes in their work field.
In the light of the given statements, choose the correct alternative:
a. Statement 1 is true and statement 2 is false
b. Statement 1 is false and statement 2 is true
c. Both statements 1 and 2 are true
d. Both statements 1 and 2 are false
Ans. Option (c)
iv. Ms. Ramanpreet has started a new business venture, she intends to spend a huge amount on ‘on-the-job training’ of her workers before putting them to work. It exhibits the right step in the direction of Human Capital Formation.
Spot which of the following does not directly contribute to the process of human capital formation by Ms. Ramanpreet:-
a. adds skills and expertise
b. improves efficiency
c. ensures gender equity
d. increases output productivity
Ans. Option (c)
v. Match the situations given in Column I with their respective implications given in Column II:
(Choose the correct alternative)
| Column I | Column II |
| A. Migration | i. reduced in per capita economic growth |
| B. Low level of academic standards | ii. An imbalance between demand and supply of human resource |
| C. Population- High Growth rate | iii. Brain Drain |
| D. Lack of proper manpower planning | iv. Mismatch between required skill and academic standards |
a. A-ii; B-iii; C-iv; D-i
b. A-iii; B-iv; C-i; D-ii
c. A-i; B-ii; C-iii; D-iv
d. A-ii; B-iv, C-i; D-iii
Ans. Option (b)
vi. Which of the following is the CORRECT difference between physical and human capital?
a. Physical capital can be sold but human capital cannot be sold.
b. Physical capital cannot be separated from its owner while human capital can.
c. Physical capital provides both private and social benefits while human capital provides only social benefits.
d. The depreciation of physical capital can be arrested with more investment while human capital will continue to deplete.
Ans. Option (a)
vii. What is the nature of human capital assets?
a. Intangible
b. Tangible
c. Both (a) and (b)
d. None of the above
Ans. Option (a)
viii. On the basis of the below-mentioned information answer the following question:
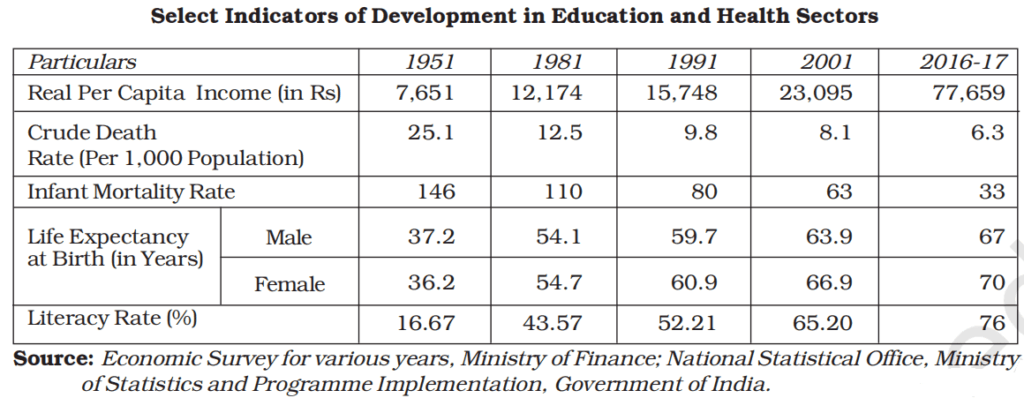
The Real Per Capita Income of India (as per the given data) has increased by _______________ (approximately) between 1951 and 2016-17. (Fill up the blank with the correct alternative)
a. 915 %
b. 1015 %
c. 815 %
d. 715 %
Ans. Option (a)
ix. Read the following statements - Assertion (A) and Reason (R):
- Assertion (A) – Human capital treats human beings as a means to an end (increase in productivity).
- Reason(R) – Human Capital Formation decreases by way of investments in education and health.
From the given alternatives choose the correct one:
Alternatives:
a. Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true and Reason (R) is the correct explanation of Assertion (A).
b. Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true and Reason (R) is not the correct explanation of Assertion (A).
c. Assertion (A) is true but Reason (R) is false.
d. Assertion (A) is false but Reason (R) is true.
Ans. Option (c)
x. Human development is _____.
a. Investment in education, health, clean environment, etc.
b. Synonym to human capital
c. Process of widening people’s choices as well as raising the level of well-being
d. Narrow concept focusing only on labor productivity
Ans. Option (c)
xi. Which of the below statements is true about human development?
a. It treats human beings as a means to an end, the end being the increase in productivity.
b. It is an end in itself.
c. It considers that investment in health and education is unproductive if it does not increase the output of goods and services.
d. Both (b) and (c)
Ans. Option (b)
xii. Which of the following could aid in human capital formation?
a. expanding the labor market by increasing the supply of jobs
b. creating larger industries with more complex equipment
c. creating open markets with increased stability
d. promoting gender equality in the family
Ans. Option (d)
xiii. Who amongst the following, has received the greatest investment in human capital formation?
a. a nurse in a clinic who is frequently absent because of his ill health
b. a 12-year-old who helps her mother with construction work
c. a 10th-pass girl who works as a store manager in a mall
d. a computer science graduate who works at a call center
Ans. Option (d)
xiv. To increase future prospects in the education sector, the Government should:
a. Focus on education for all
b. Gender equity
c. Shift from degree oriented to skill-based education
d. All of the above
Ans. Option (d)
Q. No. 2) What factors contribute to human capital formation?
Ans. The following factors contribute to human capital formation:
- Expenditure on education: spending on education by individuals is similar to spending on capital goods by companies. It is done to increase future income.
- Expenditure on health: improvement in the health of the masses increases the productive capacity and leads to qualitative improvement in human capital.
- On-the-job training: expenditure regarding on-the-job training is a source of human capital formation as the return of such expenditure, in the form of increased labor productivity, is more than the cost of it.
- Expenditure on migration: expenditure on migration may be another source of human capital formation as enhanced earnings in the migrated place is more than the increase in costs due to migration.
Q. No. 3) Explain expenditure on health as a source of human capital formation.
Ans. Health is considered to be an important input for the development of a nation as much as it is important for the development of an individual. It is important in having a productive labor force. Health expenditure directly increases the physical and mental ability of human beings and produces a healthy labor force and is, thus an important source of human capital formation.
The various forms of health expenditures are:
- preventive medicine (vaccination),
- curative medicine (medical intervention during illness),
- social medicine (spread of health literacy) and
- provision of clean drinking water and good sanitation
Q. No. 4) State, giving valid reasons whether the following statement is true or false.
Human Capital Formation gives birth to innovation, invention, and technological improvements.
Ans. The given statement is true. Human Capital Formation (investment in education/health) not only increases the productivity of the available human resources but also stimulates innovations and creates the ability to adopt and adapt to new technologies.
Q. No. 5) “Ravya was initially working as an office clerk in a firm. In the pursuit to attain position and income, she attended a few on-the-job training sessions. These sessions contributed positively to her skills and expertise.” Explain the impact of Ravya’s decision on human capital formation.
Ans. On-the-job training has become an integral part of the work environment in recent times as they add to the productive capacity of employees. Firms encourage such training, as the benefits outweigh the cost of this training. It enables employees to develop skills and adapt modern technologies/ideas.
Thus, Ravya’s decision to attend on-the-job training sessions will have a positive impact on human capital formation.
Q. No. 6) Why should (a) migration and (b) social medicine be viewed as investments in human capital? Justify with reasons.
Ans. (a) Migration takes place when people move to new places in search of opportunities, which involves a high cost.
The benefits of the migration, outweigh the expenditure and hence can be called an investment in human capital formation.
(b) Social medicine involves spreading health literacy amongst people. This creates healthy people and more productive labor.
Investments in social medicine directly lead to the increase of human capital in the labor market and hence can be called an investment in human capital formation.
Q. No. 7) Differentiate between physical capital and human capital.
Ans.
| Physical Capital | Human Capital |
| i. Physical capital implies the non-human assets of the company, such as plant and machinery, tools and equipment, office supplies, etc. that help in the process of production. | i. Human capital refers to the stock of knowledge, talent, skills, and abilities brought in by the employee to the organization. |
| ii. Tangible | ii. Intangible |
| iii. It can be traded in the market. | iii. Only the services of human capital can be sold. |
| iv. It is separable from its owner. | iv. It is not separable from its owner. |
| v. Constant use results in depreciation. | v. Ageing leads to depreciation, but it can be minimized. |
| vi. Physical capital creates only private benefits. | vi. Human capital creates both private and social benefits. |
Q. No. 8) State whether the following statements are true/false, with valid arguments:
a) Human Capital and Human Development are one and the same thing
b) India has a poor stock of technical manpower.
Ans. a) The given statement is not true to perfection. These two may sound similar but are not exactly the same. Whereas human capital considers education and health as a means to increase labor productivity, human development is based on the idea that education and health are integral to human well-being.
b) The given statement is not true. India has a rich stock of scientific and technical manpower in the world. Also, India has taken a number of steps to improve it qualitatively and ensure that they are optimally utilized.
Q. No. 9) Bring out the differences between human capital and human development.
Ans.
| Human Capital | Human Development |
| 1. Human capital considers education and health as a means to increase labor productivity. | 1. Human development is based on the idea that education and health are integral to human well-being because only when people have the ability to read and write and the ability to lead a long and healthy life, they will be able to make other choices that they value. |
| 2. Human capital treats human beings as a means to an end; the end being the increase in productivity. | 2. Here human beings are ends in themselves. Human welfare should be increased through investments in education and health even if such investments do not result in higher labor productivity. |
Q. No. 10) Why do we observe regional differences in educational attainment in India?
Ans. The per capita public expenditure on elementary education differs considerably across states from as high as Rs 34,651 in Himachal Pradesh to as low as Rs 4088 in Bihar. This leads to differences in educational opportunities and attainments across states.
Q. No. 11) What are the indicators of educational achievement in a country?
Ans. Generally, educational achievements in a country are indicated in terms of adult literacy level, primary education completion rate, and youth literacy rate.
Q. No. 12) ‘Education Commission 1964-66 had recommended that at least 6 percent of GDP must be spent on education’. How far India has been able to achieve the said goal?
Ans. Investment in the education system in India has been a woeful failure. The fact of the matter is that, in 1952 we were spending a meager 0.6% of our GDP on education which rose to only 4% in 2014. This has fallen well short of the 6% target as proposed by the Education Commission, in 1964. Moreover, throughout this period the increase in education expenditure has not been uniform and there has been irregular rise and fall.
This shows the apathy of the government towards investment in the education system. One can imagine, if the recommended 6% p.a. of the GDP would have been spent properly the present education system would have reached unforeseen heights.
Q. No. 13) “India has failed to implement the recommendations of the Education Commission of 1964 -66.” Give valid arguments in support of the given statement.
Ans. The given statement is appropriate. Over the years India has not been able to raise the educational standards to the desired level. Education Commission of 1964-66 had recommended that at least 6 % of GDP should be spent on education so as to make a noticeable rate of growth in educational achievements. However, the current expenditure level has been quite inadequate. Thus, necessary steps must be taken by the government in this direction.
Q. No. 14) In your view, is it essential for the government to regulate the fee structure in education and healthcare institutions? If so, why?
Ans. Yes, government intervention is necessary in regulating the fee structure in education and healthcare institutions.
- To maintain uniformity in the fee structure.
- To have accountability in the expenditure incurred.
- To help poor sections of the society.
- To encourage human capital formation among all poor and rich alike.
- To keep a check on the monopoly situation of private sector institutions providing education and health services.
Q. No. 15) Studies reveal that there is a difference in literacy rates between the male population and the female population implying gender inequality. Why, in your opinion education among women needs to be promoted?
Ans.
- Education empowers women. It gives them the knowledge and skills they need to make informed decisions about their lives, to participate in economic development, and to be leaders in their communities.
- Education reduces poverty. Women who are educated are more likely to be employed and to earn higher wages. This helps to lift families out of poverty and to improve their overall well-being.
- Education improves health. Women who are educated are more likely to have access to health care and to make healthy choices for themselves and their families. This leads to better health outcomes for everyone.
- Education promotes gender equality. When women are educated, they are more likely to have the same rights and opportunities as men. This helps to break down gender stereotypes and to create a more just and equitable society.
Q. No. 16) What are the main problems of human capital formation in India?
Ans.
- Education for All — Still a Distant Dream: Though literacy rates for both — adults as well as youth — have increased, still the absolute number of illiterates in India is as much as India’s population was at the time of independence.
- Gender Equity — Better than Before: The differences in literacy rates between males and females are narrowing signifying a positive development in gender equity. But the cent percent literacy rate is yet to be achieved.
- Higher Education — a Few Takers: The Indian education pyramid is steep, indicating a lesser and lesser number of people reaching the higher education level.
| Also Read: Class 12 Important Questions Class 12 Notes |
Hope you liked these Important Questions & Answers on Class 12 Economics Indian Economic Development Chapter 4 Human Capital Formation in India. Please share this with your friends and do comment if you have any doubts/suggestions to share.