As you delve into the intricacies of Class 12 Economics, Chapter 8 on Indian Economic Development emerges as a crucial chapter that unravels the nation's growth trajectory. To gain a deeper understanding of India's economic landscape, it is essential to explore its development journey in relation to its neighboring countries, Pakistan and China.
This blog post is designed to serve as a comprehensive guide for Class 12 students preparing for their 2024-25 board exams. Through a simplified approach, we will tackle the important questions and answers related to the comparative development experiences of India and its neighbors.
By embarking on this comparative analysis, you will gain valuable insights into the factors that have shaped the economic growth and social transformations of these three nations. This comparative perspective will not only enhance your understanding of Indian economic development but also equip you with the knowledge to excel in your board exams.

| Board | CBSE and State Boards |
| Class | 12 |
| Subject | Economics |
| Book Name | Indian Economic Development (IED) |
| Chapter No. | 8 |
| Chapter Name | Comparative Development Experiences of India and its Neighbours |
| Type | Important Questions & Answers |
| Session | 2024-25 |
“It is during our darkest moments that we must focus to see the light.”
— Aristotle Onassis
Comparative Development Experiences of India and its Neighbours Class 12 Questions & Answers
Q. No. 1) Multiple Choice Questions (MCQs):
i. Under the Great Leap Forward (GLF) campaign in China initiated in 1958, people were encouraged to set up industries in their backyards. Identify the primary goods these backyard industries would have produced.
a. perishable food items
b. small car parts
c. plastic toys
d. textiles
Ans. Option (a)
ii. ‘China has performed exceedingly well in various health and economic indicators.’
Identify which of the following is not a health indicator.
a) Infant Mortality Rate (per 1000 live births)
b) Life Expectancy at Birth (years)
c) Percentage of people below the poverty line (National)
d) Maternal Mortality Rate (per 1 lakh births)
Ans. Option (c)
iii. Under _________ in China, farmers and industrial units were required to buy and sell fixed quantities of inputs and outputs on the basis of prices fixed by the government, and the rest were purchased and sold at market prices. (Choose the correct alternative to fill up the blank)
a) Commune System
b) Great Leap Forward
c) Dual Pricing
d) Great Proletarian Cultural Revolution
Ans. Option (c)
iv. ‘GLF’ with respect to the People’s Republic of China referred to as ______(Choose the correct alternative).
a) Giant Leap Forward
b) Great Lead Forum
c) Great Leap Forward
d) Giant Lead Forum
Ans. Option (c)
v. Read the following statement -Assertion (A) and Reason (R). Choose one of the correct alternatives given below:
Assertion (A): In the late 1970s, China’s population growth rate had sharply declined.
Reason(R): China has witnessed an increase in the proportion of elderly people owing to stringent family planning programs.
Alternatives:
a) Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true and Reason (R) is the correct explanation of Assertion (A).
b) Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true and Reason (R) is not the correct explanation of Assertion (A).
c) Assertion (A) is true but Reason (R) is false.
d) Assertion (A) is false but Reason (R) is true.
Ans. Option (d)
vi. From the set of events/systems given in column I and the corresponding relevant fact given in column II, about China, choose the correct pair of statements:
| Column I | Column II |
| A. Great Leap Forward | i. Cultivating land Collectively |
| B. Commune System | ii. Opening of the Industries in their homes |
| C. Proletarian Cultural Revolution | iii. Students were sent to work and learn from the countryside |
| D. Economic Reforms in China | iv. 1988 |
Alternatives:
a) A - i
b) B - ii
c) C - iii
d) D – iv
Ans. Option (c)
vii. ______ adopted the “One Child Policy” as a measure to control the population. (Choose the correct alternative)
a. India
b. Pakistan
c. China
d. Russia
Ans. Option (c)
viii. China has a low-density of population compared to India and Pakistan, due to the:
a. One child policy
b. Urbanization
c. Vast geographical area
d. All of the above
Ans. Option (c)
ix. _____ and _____ are the reasons for the slowdown of the Pakistan economy since independence.
- political instability
- over-dependence on remittances from abroad
- stable performance of the agriculture sector
- growth of the service sector
Alternatives:
a) 1 and 2
b) 2 and 3
c) 3 and 4
d) 1 and 4
Ans. Option (a)
x. Introduction of Economic Reform in Pakistan took place in…………… (Choose the correct alternative)
a) 1978
b) 1980
c) 1988
d) 1991
Ans. Option (c)
xi. Arrange the following events of China in chronological order and choose the correct alternative:
- Great Proletarian Cultural Revolution
- Great Leap Forward campaign
- Introduction of Economic Reforms
- First five-year plan
Choose the correct alternative:
a) 2, 4, 3, 1
b) 4, 2, 1, 3
c) 2, 4, 1, 3
d) 4, 1, 2, 3
Ans. Option (b)
xii. The main objective of China's One Child Policy, which was implemented from 1979 to 2016 was:
a) to provide financial incentives for families with multiple children
b) to promote gender equality by limiting the number of male children
c) to control the population growth and address overpopulation concerns
d) to encourage families to have more children and increase the population
Ans. Option (c)
xiii. The growth process causes a shift in sectoral share in output and employment. In a classical growth pattern as the process of growth gathers momentum, the percentage share of output and employment in the primary sector tends to ____ and that of the secondary and tertiary sectors tends to _____.
a. increase, decrease
b. Decrease, increase
c. Remains constant, increase
d. Increase, remains unchanged
Ans. Option (b)
xiv. Identify the developmental initiatives oriented by Pakistan during the 1970s and 80s that helped the country stimulate economic growth.
a. agrarian reforms
b. de-nationalization
c. import substitution
d. investment in education and health
Ans. Option (b)
xv. Read the following statements carefully.
- Statement 1: Both India and Pakistan initiated their economic reforms without any external pressures.
- Statement 2: Pakistan has successfully implemented the SEZ policy and reaped its benefits using the Export Promotion policy.
In the light of the given statements, choose the correct alternative:
a) Statement 1 is true and statement 2 is false
b) Statement 1 is false and statement 2 is true
c) Both statements 1 and 2 are true
d) Both statements 1 and 2 are false
Ans. Option (d)
xvi. From the set of the events given in column I and corresponding facts given in Column II, choose the correct pair of statements:
| COLUMN I | COLUMN II |
| i. Dual Pricing | A. Economic Reforms of 1991 |
| ii. Setting up of Special Economic Zones in China | B. To attract Foreign Direct Investment |
| iii. Commune System | C. Backyard based Industrial production units |
| iv. Great Proletarian Cultural Revolution | D. Collective Farming |
Alternatives:
a) i – A
b) ii – B
c) iii – C
d) iv – D
Ans. Option (b)
xvii. From the set of the events given in column I and corresponding facts given in Column II, choose the correct pair of statements:
| Column I | Column II |
| A. Adoption of a mixed economic system | I. The common development policy of India and China |
| B. Introduction of economic reforms in China | II. Imposed by the World Bank |
| C. Great Leap Forward Campaign | III. Focussed on massive industrialization |
| D. First Five-Year Plan of Pakistan | IV. Announced in 1953 |
Alternatives:
a) A-I
b) B-II
c) C-III
d) D-IV
Ans. Option (c)
xviii. Liberty indicators may be defined as:
a. The extent of democratic participation in social and political decision-making
b. The extent of constitutional protection given to rights of citizens
c. The extent of constitutional protection of the independence of the judiciary and the rule of the law
d. All of the above
Ans. Option (d)
xix. Economic reforms adopted by Pakistan in 1988 yielded spectacular results and the Pakistan economy was performing well. But even after the spectacular growth trajectory, Pakistan seems to have slipped into poverty. The re-emergence of poverty in Pakistan is due to:
a. Opening up the economy to global investors
b. Large dependence on remittance from abroad
c. Shift from protection to competition
d. None of the above
Ans. Option (b)
Q. No. 2) Explain the Great Leap Forward campaign of China as initiated in 1958.
Ans.
- Initiated in 1958 aimed at industrializing the country on a massive scale.
- People were encouraged to set up industries in their backyards.
- In rural areas, communes were started. Under the Commune system, people collectively cultivated lands.
- GLF campaign met with many problems:
- A Severe drought caused havoc in China killing about 30 million people.
- When Russia had conflicts with China, it withdrew its professionals who had earlier been sent to China to help in the industrialization process.
Q. No. 3) “In the late 1970s, China introduced the One-child policy that led to arrest in the population coupled with skewed sex ratio.” Justify the given statement with valid arguments in support of your answer.
Ans. China is the most populous country in the world. Its annual population growth rate was very high. The one-child norm introduced in China in the late 1970s is the major reason for the fall in the population growth rate.
However, this measure led to a decline in the sex ratio. The number of females per 1000 males in China is approximately 949. The one-child policy and prevalent son preference is the prime reason behind the skewed sex ratio.
Q. No. 4) Given below are some statistics related to India, China, and Pakistan.
| Country | Population (millions) | Fertility rate | Urbanization (%) |
| India | 1352 | 2.2 | 34 |
| China | 1393 | 1.7 | 59 |
| Pakistan | 212 | 3.6 | 37 |
Compare and contrast China's demographic statistics with its neighbors.
Ans.
- China has a lower fertility rate than its neighbors which can be attributed to its one-child policy
- The low fertility rate has resulted in an increased ratio of the aging population in China accompanied by a very low growth rate
- India would overtake China as the most populous nation in the coming years
- a greater percentage of the population in China would have access to urban amenities such as well-developed social infrastructure, improved transport and communication networks
- Both India and Pakistan have a relatively larger population that is probably engaged in agricultural activities.
Q. No. 5) Compare and analyze the given data of India and China with valid arguments.
Annual Growth of Gross Domestic Product (%), 1980-2017
| COUNTRY | 1980-90 | 2015-2017 |
| India | 5.7 | 7.3 |
| China | 10.3 | 6.8 |
Ans. The given data shows that China has gained economic strength over the years. When many developed countries were finding it difficult to maintain a growth rate of even 5%, China was able to maintain near double-digit growth during the decade of the 1980s. The growth rate of China has decelerated to an average of 6.8%, over the period 2015-17.
In the recent past, India has posted a decent rise in the growth rate. While India had maintained a reasonable growth rate of 5.7% in the decade of the 1980’s it has shown great caliber and character in the period 2015-17 by registering an average of 7.3%, over the period 2015-17.
Nevertheless, the Indian elephant has to travel a long distance before it can present itself as a real threat to the growth story of the Chinese dragon.
Q. No. 6) Answer the following questions on the basis of the following data:
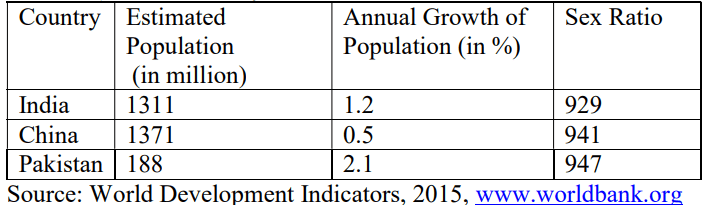
a) Comment upon the population growth rates among the three countries.
b) Which country has the most skewed sex ratio?
Ans. a) The given data shows that the annual growth rate of the population is maximum in Pakistan standing at 2.1%, whereas; the same stands at a meager 0.5% in the case of China (which might be a direct result of the One Child Policy adopted). The annual population growth rate of India is in the danger zone of more than 1% p.a. India will be overtaking China as the most populous country in the world in the near future.
b) Amongst the three countries stated above, India has the most skewed data sex ratio (929 females per 1000 males). This is one of the major concerns for the demographers in India.
Q. No. 7) Read the following text carefully and answer the questions given below:
SINO-PAK FRIENDSHIP CORRIDOR
The China-Pakistan Economic Corridor (CPEC) has deepened the decades-long strategic relationship between the two nations. But it has also sparked criticism for burdening Pakistan with mountains of debt and allowing China to use its debt strategic assets of Pakistan.
The foundations of CPEC, part of China’s Belt and Road Initiative, were laid in May 2013. At the time, Pakistan was reeling under weak economic growth. China committed to play an integral role in supporting Pakistan’s economy.
Pakistan and China have a strategic relationship that goes back decades. Pakistan turned to China at a time when it needed a rapid increase in external financing to meet critical investments in hard infrastructure, particularly power plants and highways. CPEC’s early harvest projects met this need, leading to a dramatic increase in Pakistan’s power generation capacity, bringing an end to supply-side constraints that had made rolling blackouts a regular occurrence across the country.
Pakistan leaned into CPEC, leveraging Chinese financing and technical assistance in an attempt to end power shortages that had paralyzed its country’s economy. Years later, China’s influence in Pakistan has increased at an unimaginable pace.
China As Pakistan’s Largest Bilateral Creditor: China’s ability to exert influence on Pakistan’s economy has grown substantially in recent years, mainly due to the fact that Beijing is now Islamabad’s largest creditor. According to documents released by Pakistan’s finance ministry, Pakistan’s total public and publicly guaranteed external debt stood at $44.35 billion in June 2013, just 9.3 percent of which was owed to China. By April 2021, this external debt had ballooned to $90.12 billion, with Pakistan owing 27.4 percent —$24.7 billion — of its total external debt to China, according to the International Monetary Fund (IMF).
Additionally, China provided financial and technical expertise to help Pakistan build its road infrastructure, expanding north-south connectivity to improve the efficiency of moving goods from Karachi all the way to Gilgit-Baltistan (POK). These investments were critical in better integrating the country’s ports, especially Karachi, with urban centers in Punjab and Khyber Pakhtunkhwa provinces.
Despite power asymmetries between China and Pakistan, the latter still has tremendous agency in determining its own policies, even if such policies come at the expense of the long-term socioeconomic welfare of Pakistani citizens.
(https://www.usip.org/publications/2021/05/pakistans-growing-problem-its-china-economic-corridor - Modified)
1. Outline and discuss any two economic advantages of China Pakistan Economic Corridor (CPEC) accruing to the economy of Pakistan.
2. Analyse the implication of the bilateral ‘debt-trap’ situation of Pakistan vis-à-vis the Chinese Economy.
Ans. 1. Economic advantages of China Pakistan Economic Corridor (CPEC) to the economy of Pakistan are:
- China provided financial and technical expertise to help Pakistan build its road infrastructure, supporting employment and income in the economy
- CPCE has led to a massive increase in the power generation capacity of Pakistan. It has brought an end to supply-side constraints in the nation, which had made blackouts a regular phenomenon across the country.
2. China has become famous for its ‘Debt Trap Diplomacy’ in recent times. Under this China provides financial and technical expertise/assistance to help various nations to bring them under its direct or indirect influence.
The first and foremost implication of the diplomacy is that Beijing has now become Islamabad’s largest creditor. According to documents released by Pakistan’s finance ministry, its total public external debt stood at $44.35 billion in June 2013, just 9.3 percent of which was owed to China. By April 2021, this external debt had ballooned to $90.12 billion, with Pakistan owing 27.4 percent —$24.7 billion — of its total external debt to China, according to the IMF.
Q. No. 8) Compare and analyze the following information related to the Imports and Exports of the three neighboring nations:
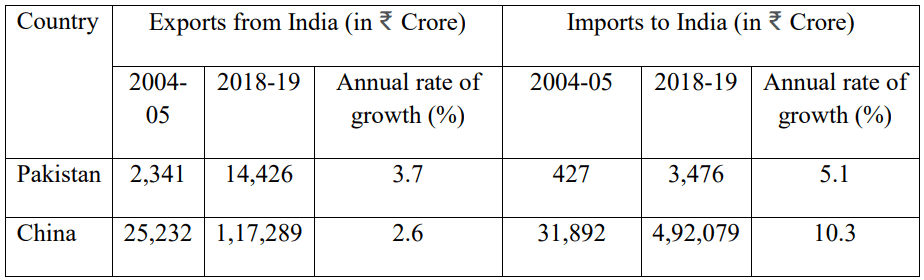
Ans. The above table shows that during the given periods the Exports from India to Pakistan have increased at an annualized rate of 3.7 % while the same with China shows 2.6% growth. On the other hand, India’s imports from China accounted for a massive 10.3 %. The corresponding figure with Pakistan witnessed an average of 5.1% respectively.
The situation indicates that Indian imports from China are too high in comparison to the exports to China. This shows that the Indian economy was over-dependent on the Chinese economy for goods and services, over the given period of time. Whereas, in the case of Pakistan gap is quite narrow, which may be due to various reasons.
Q. No. 9) Define the liberty indicator. Give some examples of liberty indicators.
Ans. Liberty indicators are measures or criteria used to evaluate the degree of freedom and individual rights within a society.
Here are some liberty indicators:
- Democratic Participation in Decision-Making
- Constitutional Protection of Citizens' Rights
- Independence of the Judiciary
- Rule of Law
Q. No. 10) Give reasons for the slow growth and re-emergence of poverty in Pakistan.
Ans. The reasons for the slow-down of growth and re-emergence of poverty in Pakistan’s economy, are:
- political instability,
- over-dependence on remittances and foreign aid
- volatile performance of the agriculture sector.
| Also Read: Class 12 Important Questions Class 12 Notes |
Hope you liked these Important Questions Answers on Class 12 Economics Indian Economic Development Chapter 8 Comparative Development Experiences of India and its Neighbours. Please share this with your friends and do comment if you have any doubts/suggestions to share.
These questions will come in board’s
Thanks!! It helped a lot in revising this chapter .