Feeling the heat as the CBSE Class 12 Chemistry exam (Feb 27, 2025) approaches? Worry not, future chemistry whizzes! We have a secret weapon in our arsenal: the 2023 Class 12 Chemistry Topper's Answer Sheet, officially released by CBSE as a model answer. This isn't just any answer sheet; it's a treasure trove of insights and strategies crafted by someone who aced the exam.
Think of it as a sneak peek into the mind of a champion. Analyze their approach, understand their thought process, and glean valuable tips to elevate your own answers. But remember, this isn't about rote memorization; it's about unlocking a deeper understanding and applying it effectively.
The best part? We've made it even easier to access this knowledge. To download the official PDF of both the 2023 Class 12 Chemistry Question Paper and Topper's Answer Sheet, click the link below. Dive in, analyze, and prepare to conquer your exam with A+ confidence!
| Class | 12 |
| Board | CBSE |
| Subject | Chemistry |
| Exam Date | 27/02/2024 |
| Content-Type | 2023 Topper's Answer Sheet |
| Session | 2024-25 |
| Official Website | https://www.cbse.gov.in/ |


SECTION A
Questions no. 1 to 18 are Multiple Choice (MCQ) type Questions, carrying 1 mark each. 18x1=18
1. The colligative property used for the determination of molar mass of polymers and proteins is:
(a) Osmotic pressure
(b) Depression in freezing point
(c) Relative lowering in vapour pressure
(d) Elevation is boiling point
2. Low concentration of oxygen in the blood and tissues of people living at high altitude is due to:
(a) high atmospheric pressure
(b) low temperature
(c) low atmospheric pressure
(d) both low temperature and high atmospheric pressure
3. The correct cell to represent the following reaction is:
Zn + 2Ag+ → Zn2+ + 2Ag
(a) 2Ag | Ag+ || Zn | Zn2+
(b) Ag+ | Ag || Zn2+ | Zn
(c) Ag | Ag+ || Zn | Zn2+
(d) Zn | Zn2+ || Ag+ | Ag
4. △G and E° cell for a spontaneous reaction will be :
(a) positive, negative
(b) negative, negative
(c) negative, positive
(d) positive, positive
5. Which of the following is affected by catalyst?
(a) △H
(b) △G
(c) Ea
(d) △S
6. The order of the reaction H2 (g) + Cl2 (g) (hv)→ 2HCl (g) is:
(a) 2
(b) 1
(c) 0
(d) 3
7. The most common and stable oxidation state of a Lanthanoid is :
(a) + 2
(b) + 3
(c) + 4
(d) + 6
8. The compounds [Co(SO4) (NH3)5 ]Br and [Co(Br)(NH3)5]SO4 represent:
(a) optical isomerism
(b) linkage isomerism
(c) ionisation isomerism
(d) coordination isomerism
9. The synthesis of alkyl fluoride is best obtained from:
(a) Free radicals
(b) Swartz reaction
(c) Sandmeyer reaction
(d) Finkelstein reaction
10. In the reaction R-OH + HCl (ZnCl2) → RCl + H2O, what is the correct order of reactivity of alcohol?
(a) 1° < 2° < 3°
(b) 1° > 3° > 2°
(c) 1° > 2° > 3°
(d) 3° > 1° > 2°
11. CH3CONH2 on reaction with NaOH and Br2 in alcoholic medium gives:
(a) CH3COONa
(b) CH3NH2
(c) CH3CH2Br
(d) CH3CH2NH2
12. Which of the following is least basic?

13. The glycosidic linkage involved in linking the glucose units in amylase part of starch is :
(a) C1-C6 α linkage
(b) C1-C6 β linkage
(c) C1-C4 α linkage
(d) C1-C4 β linkage
14. An α-helix is a structural feature of :
(a) Sucrose
(b) Starch
(c) Polypeptides
(d) Nucleotides
For Questions number 15 to 18, two statements are given one labelled as Assertion (A) and the other labelled as Reason (R). Select the correct answer to these questions from the codes (a), (b), (c), and (d) as given below.
(a) Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true and Reason (R) is the correct explanation of the Assertion (A).
(b) Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true, but Reason (R) is not the correct explanation of the Assertion (A).
(c) Assertion (A) is true, but Reason (R) is false.
(d) Assertion (A) is false, but Reason (R) is true.
15. Assertion (A): -NH2 group is o- and p-directing in electrophilic substitution reactions.
Reason (R): Aniline cannot undergo Friedel-Crafts reaction.
16. Assertion (A): Acetylation of aniline gives a monosubstituted product.
Reason (R): Activating effect of -NHCOCH3 group is more than that of amino group.
17. Assertion (A): The molecularity of the reaction H2 + Br2 → 2HBr appears to be 2.
Reason (R): Two molecules of the reactants are involved in the given elementary reaction.
18. Assertion (A): Low spin tetrahedral complexes are rarely observed.
Reason (R): Crystal field splitting energy is less than pairing energy for tetrahedral complexes.
Ans.


SECTION B
19. What is Henry's Law? Give one application of it.
Ans.


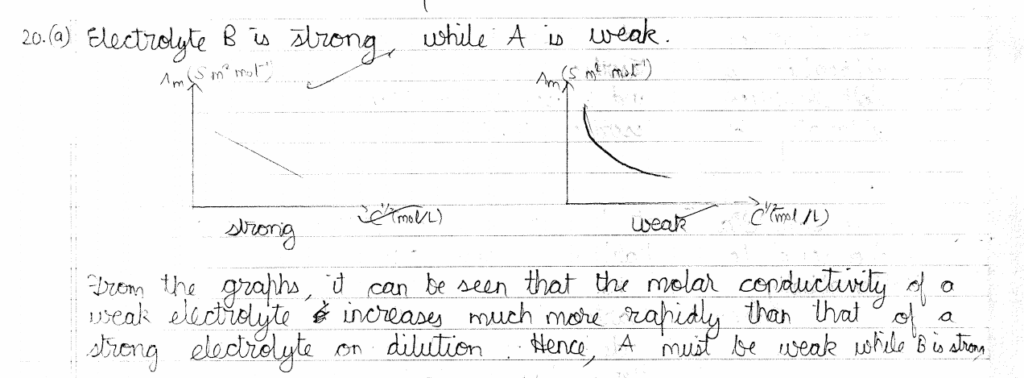
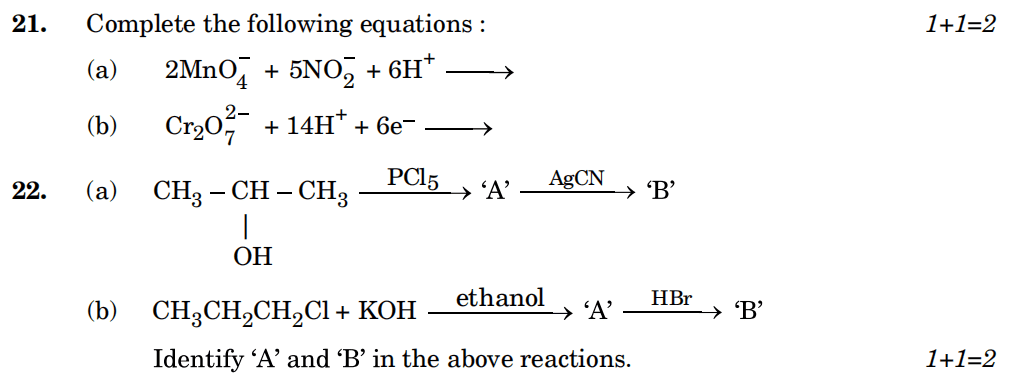
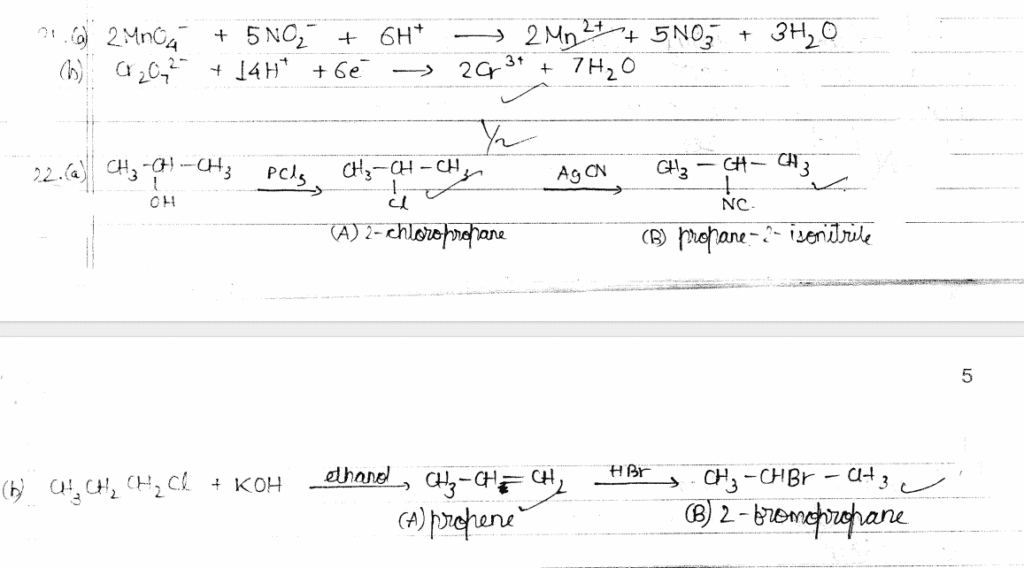
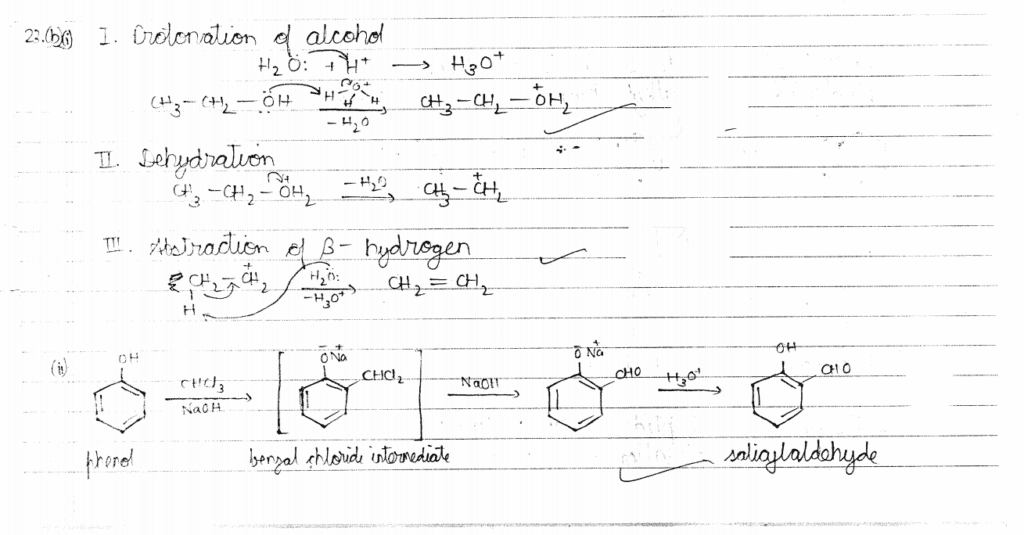
23. (a) Account for the following: 1+1=2
(i) Phenol is a stronger acid than an alcohol.
(ii) The boiling point of alcohols decreases with increase in branching of alkyl chain.
OR
(b) (i) Write the mechanism of the following reaction :
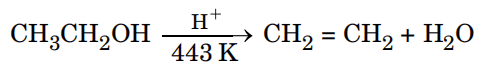
(ii) Write the equation involved in Reimer-Tiemann reaction. 1+1=2
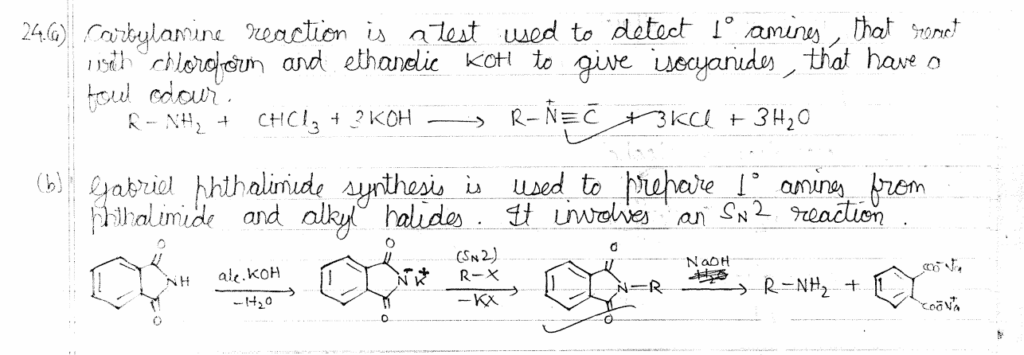
24. Explain briefly: 1+1=2
(a) Carbylamine reaction
(b) Gabriel phthalimide synthesis
25. (a) Write chemical reaction to show that open structure of D-glucose contains the straight chain.
(b) What type of linkage is responsible for the formation of protein?

SECTION C
26. (a) Differentiate between Ideal solution and Non-ideal solution.
(b) 30g of urea is dissolved in 846g of water. Calculate the vapour pressure of water for this solution if vapour pressure of pure water at 298 K is 23.8 mm Hg.


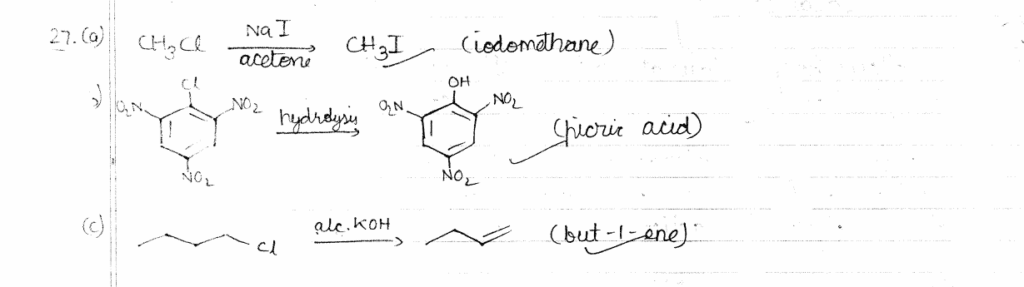
27. Write main product formed when: 3x1=3
(a) Methyl chloride is treated with NaI/Acetone.
(b) 2,4,6-trinitrochlorobenzene is subjected to hydrolysis.
(c) n-Butyl chloride is treated with alcoholic KOH.
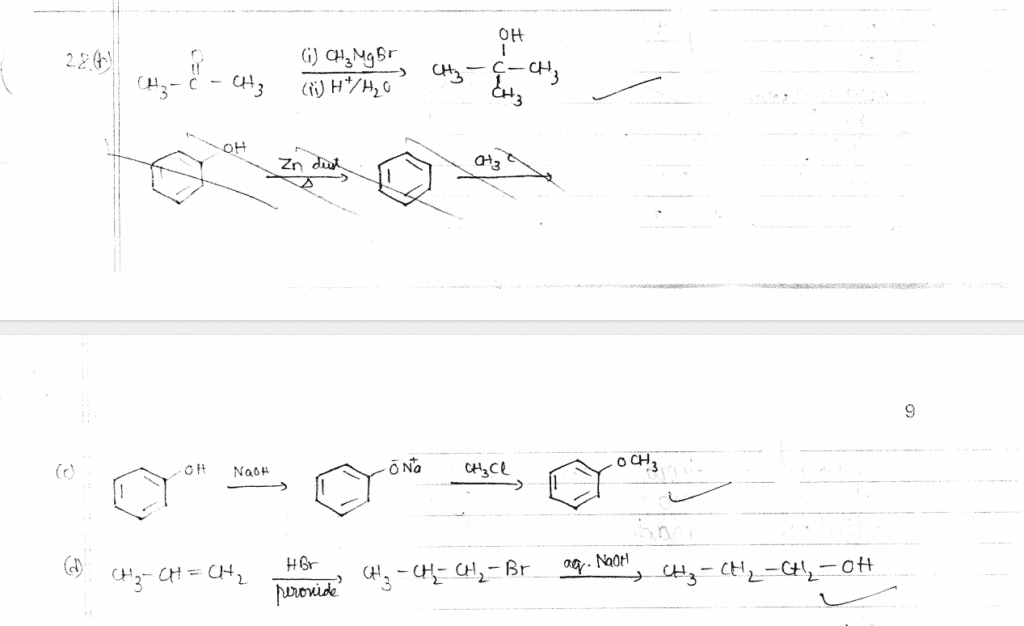
28. How do you convert the following : (Any three) 3x1=3
(a) Phenol to picric acid
(b) Propanone to 2-Methylpropan-2-ol
(c) Phenol to anisole
(d) Propene to Propan-1-ol
29. (a) Explain why : 3x1=3
(i) Carboxyl group in benzoic acid is meta directing.
(ii) Sodium bisulphite is used for the purification of aldehydes and ketones.
(iii) Carboxylic acids do not give characteristic reactions of carbonyl group.
OR
(b) An organic compound 'A', having molecular formula C3H8O on treatment with Cu at 573K, gives B. B does not reduce Fehling's solution but gives a yellow precipitate of the compound 'C' with I2 /NaOH. Deduce the structures of A, B, and C.
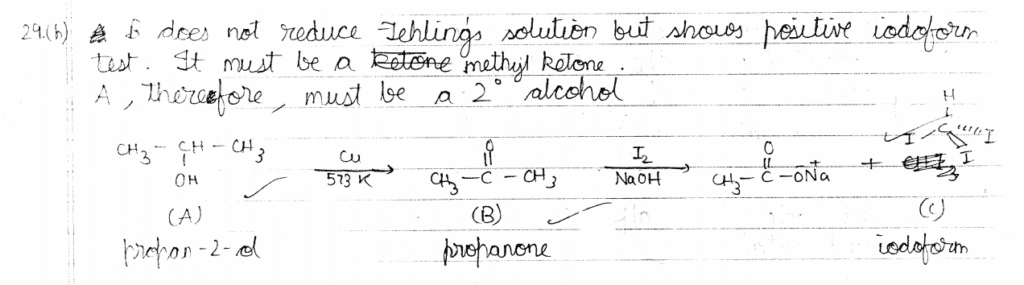
30. (a) What are the hydrolysis products of (i) Lactose, (ii) Maltose?
(b) Give the basic structural difference between starch and cellulose. 2+1=3

SECTION D
The following questions are case-based questions. Read the case carefully and answer the questions that follow.
31. The rate of reaction is concerned with decrease in concentration of reactants or increase in the concentration of products per unit time. It can be expressed as instantaneous rate at a particular instant of time and average rate over a large interval of time. Mathematical representation of rate of reaction is given by rate law. Rate constant and order of a reaction can be determined from rate law or its integrated rate equation.
(i) What is average rate of reaction? 1
(ii) Write two factors that affect the rate of reaction. 1
(iii) (1) What happens to rate of reaction for zero order reaction?
(2) What is the unit of k for zero order reaction? 2x1=2
OR
(iii) (1) For a reaction P + 2Q → Products
Rate = k[P]1/2[Q]1. What is the order of the reaction?
(2) Define pseudo first-order reaction with an example. 2x1=2

32. In coordination compounds, metals show two types of linkages, primary and secondary. Primary valencies are ionisable and are satisfied by negatively charged ions. Secondary valencies are non-ionisable and are satisfied by neutral or negative ions having lone pair of electrons. Primary valencies are non-directional while secondary valencies decide the shape of the complexes.
(i) If PtCl2 . 2NH3 does not react with AgNO3 , what will be its formula? 1
(ii) What is the secondary valency of [Co(en)3 ]3+? 1
(iii) (1) Write the formula of Iron(III)hexacyanidoferrate(II).
(2) Write the IUPAC name of [Co(NH3)5Cl]Cl2. 2x1=2
OR
(iii) Write the hybridization and magnetic behaviour of [Ni(CN)4]2-. 2
[Atomic number : Ni = 28]

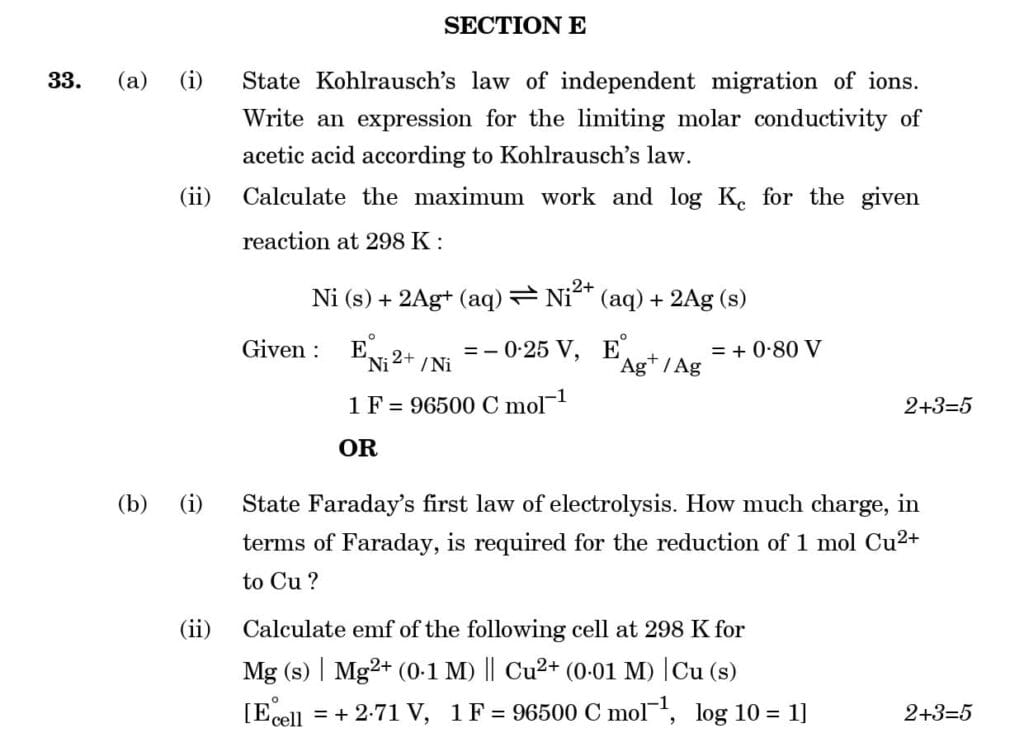

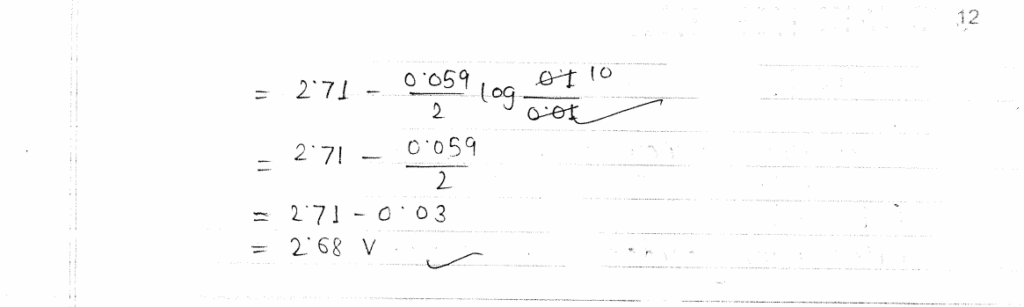





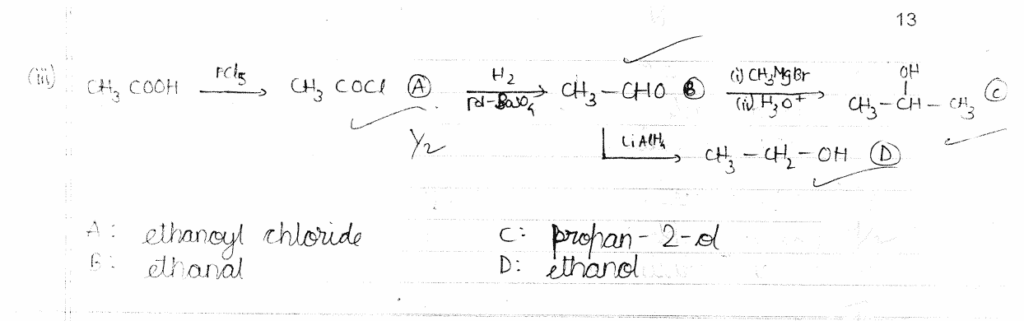
PDF of CBSE Class 12 Chemistry Board's Question Paper 2023
PDF of CBSE Class 12 Chemistry Topper's Answer Sheet



Sir music ka topper ka answer sheet bhejiye music vocal ka