Scoring high in CBSE Class 10 Science requires a clear understanding of concepts and effective answer-writing skills. To help students understand the best way to present answers in the board exams, we have provided the CBSE Class 10 Science 2024 Question Paper along with the topper’s answer sheet. This will give you an insight into the writing style, presentation, and key points that fetch full marks.
📌 Why Check the Topper’s Answer Sheet?
- Perfect Answer Structure – Learn how to frame answers concisely and effectively.
- Proper Use of Diagrams – See how toppers use labeled diagrams to enhance their answers.
- Stepwise Marks Allocation – Understand how stepwise marking helps in scoring full marks.
- Time Management – Get an idea of how toppers complete the paper within the time limit.
- Use of Keywords – Identify the keywords that examiners look for while checking answer sheets.
CBSE Class 10 Science 2024 Question Paper PDF
We have attached the official CBSE Class 10 Science 2024 Question Paper below. You can download the PDF version to practice and compare your answers with those of the toppers.
CBSE Class 10 Science 2024 Topper’s Answer Sheet
Below are screenshots of the actual answer sheets of the toppers, showing how they have written each answer to maximize their marks. Pay close attention to:
✔️ Neat Handwriting & Proper Spacing
✔️ Stepwise Answering for Numerical Questions
✔️ Use of Diagrams in Biology and Physics Questions
✔️ Scientific Terminology & Proper Formatting
Question Paper Code: 31/5/1, Set-1, Series CABD5/5
SCIENCE
Time allowed: 3 hours
Maximum Marks: 80
General Instructions:
Read the following instructions very carefully and strictly follow them:
(i) This question paper comprises 39 questions. All questions are compulsory.
(ii) This question paper is divided into five sections – A, B, C, D, and E.
(iii) Section A – Questions No. 1 to 20 are multiple-choice questions. Each question carries 1 mark.
(iv) Section B – Questions No. 21 to 26 are very short answer type questions. Each question carries 2 marks. Answer to these questions should be in the range of 30 to 50 words.
(v) Section C – Questions No. 27 to 33 are short answer type questions. Each question carries 3 marks. Answer to these questions should be in the range of 50 to 80 words.
(vi) Section D – Questions No. 34 to 36 are long answer type questions. Each question carries 5 marks. Answer to these questions should be in the range of 80 to 120 words.
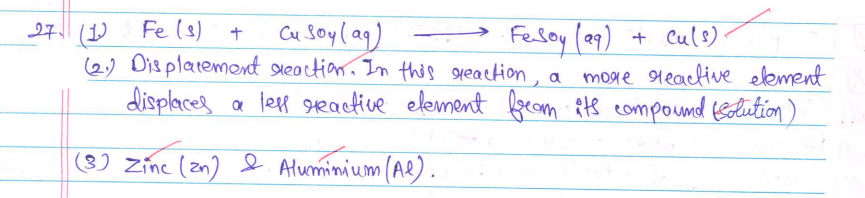
(vii) Section E – Questions No. 37 to 39 are of 3 source-based/case-based units of assessment carrying 4 marks each with sub-parts.
(viii) There is no overall choice. However, an internal choice has been provided in some sections. Only one of the alternatives has to be attempted in such questions.
SECTION A
Select and write the most appropriate option out of the four options given for each of the questions no. 1 to 20. 20×1=20
1. To balance the following chemical equation, the values of the coefficients ( x, y ) and ( z ) must be respectively:
x Zn(NO₃)₂ → y ZnO + z NO₂ + O₂
(A) 4, 2, 2
(B) 4, 4, 2
(C) 2, 2, 4
(D) 2, 4, 2
2. Which of the following is a redox reaction, but not a combination reaction?
(A) C + O₂ → CO₂
(B) 2 H₂ + O₂ → 2 H₂O
(C) 2 Mg + O₂ → 2 MgO
(D) Fe₂O₃ + 3 CO → 2 Fe + 3 CO₂
3. The salt present in tooth enamel is:
(A) Calcium phosphate
(B) Magnesium phosphate
(C) Sodium phosphate
(D) Aluminium phosphate
4. An aqueous solution of sodium chloride is prepared in distilled water. The pH of this solution is:
(A) 6
(B) 8
(C) 7
(D) 3
5. A metal ‘X’ is used in thermit process. When ‘X’ is heated with oxygen, it gives an oxide ‘Y’, which is amphoteric in nature. ‘X’ and ‘Y’ respectively are:
(A) Mn, MnO₂
(B) Al, Al₂O₃
(C) Fe, Fe₂O₃
(D) Mg, MgO
6. The process in which transport of soluble products of photosynthesis takes place in plants is known as:
(A) Transpiration
(B) Evaporation
(C) Conduction
(D) Translocation
7. The correct sequence of events when someone’s hand touches a hot object unconsciously:
(A) Receptors in skin → Motor neuron → Relay neuron → Sensory neuron → Effector muscle in arm
(B) Receptors in skin → Relay neuron → Sensory neuron → Motor neuron → Effector muscle in arm
(C) Receptors in skin → Sensory neuron → Relay neuron → Motor neuron → Effector muscle in arm
(D) Receptors in skin → Sensory neuron → Effector muscle in arm → Motor neuron → Relay neuron
8. Sense organ in which olfactory receptors are present is:
(A) Nose
(B) Skin
(C) Tongue
(D) Inner ear
9. The incorrect statement about placenta is:
(A) It is a disc embedded in the uterine wall.
(B) It contains villi on the embryo’s side of the tissue.
(C) It has a very small surface area for glucose and oxygen to pass from mother to the embryo.
(D) The embryo gets nutrition from the mother’s blood through it.
10. Select from the following the conditions responsible for the rapid spread of bread mould on a slice of bread:
- (i) Formation of a large number of spores
- (ii) Presence of moisture and nutrients in bread
- (iii) Low temperature
- (iv) Presence of hyphae
(A) (i) and (ii)
(B) (ii) and (iv)
(C) (ii) and (iii)
(D) (iii) and (iv)
11. How will the image formed by a convex lens be affected, if the upper half of the lens is wrapped with a black paper?
(A) The size of the image formed will be one-half of the size of the image due to complete lens.
(B) The image of the upper half of the object will not be formed.
(C) The brightness of the image will reduce.
(D) The lower half of the inverted image will not be formed.
12. The phenomena of light involved in the formation of rainbow are:
(A) Refraction, reflection, and dispersion
(B) Refraction, dispersion, and internal reflection
(C) Reflection, dispersion, and internal reflection
(D) Refraction, dispersion, scattering, and total internal reflection
13. The colour of light for which the refractive index of glass is minimum, is:
(A) Red
(B) Yellow
(C) Green
(D) Violet
14. The current-carrying device which produces a magnetic field similar to that of a bar magnet is:
(A) A straight conductor
(B) A circular loop
(C) A solenoid
(D) A circular coil
15. A uniform magnetic field exists in the plane of paper as shown in the diagram.
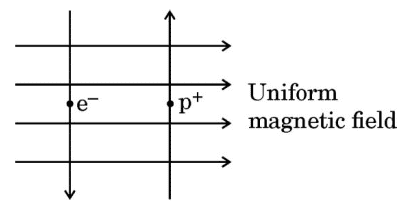
In this field, an electron (e-) and a positron (p+) enter as shown. The electron and positron experience forces:
(A) both pointing into the plane of the paper.
(B) both pointing out of the plane of the paper.
(C) pointing into the plane of the paper and out of the plane of the paper respectively.
(D) pointing out of the plane of the paper and into the plane of the paper respectively.
16. Which one of the following is not a natural ecosystem?
(A) Pond ecosystem
(B) Grassland ecosystem
(C) Forest ecosystem
(D) Cropland ecosystem
For Questions number 17 to 20, two statements are given — one labelled as Assertion (A) and the other labelled as Reason (R). Select the correct answer to these questions from the codes (A), (B), (C), and (D) as given below.
(A) Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true and Reason (R) is the correct explanation of the Assertion (A).
(B) Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true, but Reason (R) is not the correct explanation of the Assertion (A).
(C) Assertion (A) is true, but Reason (R) is false.
(D) Assertion (A) is false, but Reason (R) is true.
17. Assertion (A): Some vegetable oils are healthy.
Reason (R): Vegetable oils generally have long unsaturated carbon chains.
18. Assertion (A): Sex of the children will be determined by what they inherit from their mother.
Reason (R): Women have XX sex chromosomes.
19. Assertion (A): Electrons move from lower potential to higher potential in a conductor.
Reason (R): A dry cell maintains electric potential difference across the ends of a conductor.
20. Assertion (A): Ozone layer protects the surface of the Earth from harmful UV radiations.
Reason (R): Chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs) are responsible for the depletion of the ozone layer.
Ans.


SECTION B
Questions no. 21 to 26 are very short answer type questions.
21. (a) Copper powder is taken in a china dish and heated over a burner. Name the product formed and state its colour. Write the chemical equation for the reaction involved.
OR
(b) Write the chemical equation for the chemical reaction which occurs when the aqueous solutions of barium chloride and sodium sulphate react together. Write the symbols of the ions present in the compound precipitated in the reaction.
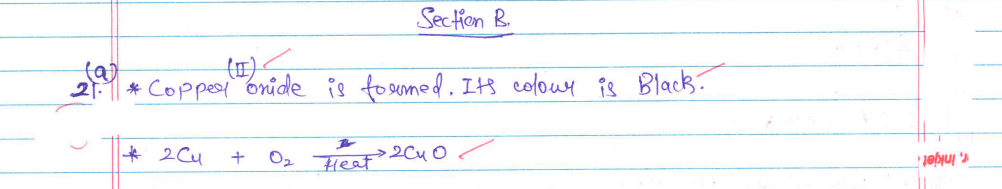
22. The melting and boiling points of carbon compounds are generally low, and they are largely non-conductors of electricity. State two conclusions based on these two properties.

23. (a) Sometimes while running, the athletes suffer from muscle cramps. Why? How is the respiration in this case different from aerobic respiration?
OR
(b) Write the other name given to lymph. State its two functions.

24. Some unicellular organisms such as Plasmodium and Leishmania differ in the manner in which they reproduce. Name and explain the reproductive process taking place in them.

25. The heat produced at a point due to the concentration of sunlight by a convex lens burns a paper.
(a) Explain why it happens.
(b) Name the term (in the context of the lens used) given to the point at which the paper starts burning. What does the bright spot formed on the paper represent?

26. An electric source can supply a charge of 500 coulomb. If the current drawn by a device is 25 mA, find the time in which the electric source will be discharged completely.
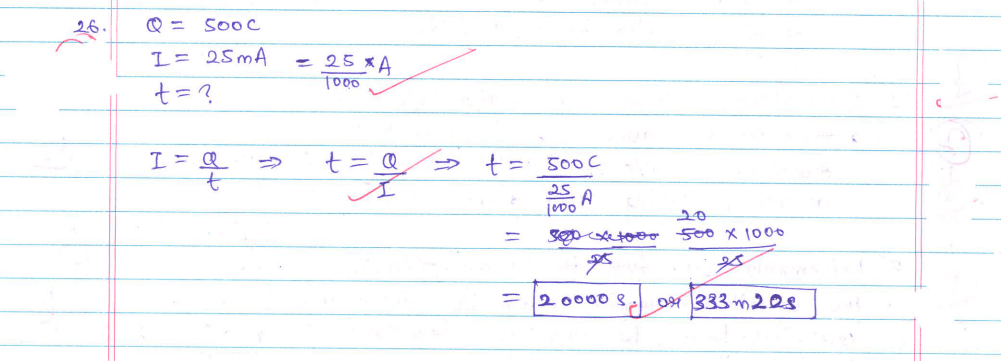
Key Takeaways from the Topper’s Answer Sheet
✅ Write to the Point: Avoid unnecessary explanations and stick to NCERT-based answers.
✅ Highlight Keywords: Use underlining or bold text to emphasize important points.
✅ Follow CBSE Marking Scheme: Answer according to the marks allotted to each question.
✅ Include Diagrams Where Required: Neat, labeled diagrams can help you score better.
✅ Solve Numericals Step by Step: Clearly mention formulas and units in Physics and Chemistry answers.
SECTION C
Questions no. 27 to 33 are short answer type questions.
27. Study the experimental set-up shown in the diagram and write the chemical equation for the chemical reaction involved.
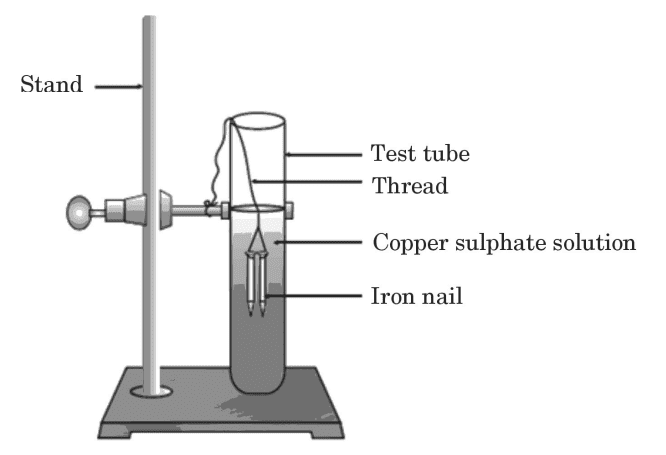
Name and define the type of reaction. List two other metals which can be used in place of iron to show the same type of reaction with copper sulphate solution.
28. Name the ore of mercury and state the form in which it is found in nature. Write the chemical equations along with the condition required for the reactions involved in the extraction of mercury from its ore.
29. Taking the example of any two animal hormones along with their gland of secretion, explain how these hormones help (i) in growth and development and (ii) regulate metabolism, in the body.

30. Mendel crossed pure tall pea plants (TT) with pure short pea plants (tt) and obtained ( F1 ) progeny. When the plants of ( F1 ) progeny were self-pollinated, plants of ( F2 ) progeny were obtained.
(a) What did the plants of ( F1 ) progeny look like? Give their gene combination.
(b) Why could the gene for shortness not be expressed in plants of ( F1 ) progeny?
(c) Write the ratio of the plants obtained in ( F2 ) progeny and state the conclusion that can be drawn from this experiment.

31. (a) Study the diagram given below and answer the questions that follow:
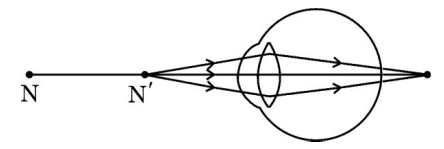
(i) Name the defect of vision depicted in this diagram stating the part of the eye responsible for this condition.
(ii) List two causes of this defect.
(iii) Name the type of lens used to correct this defect and state its role in this case
OR
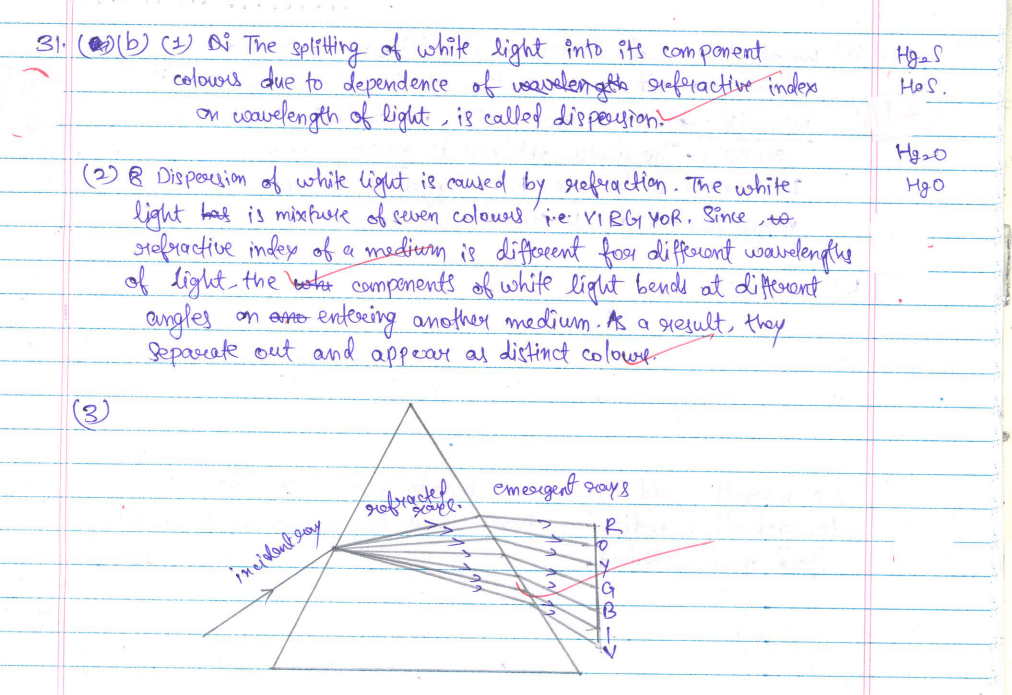
(b) What is dispersion of white light? State its cause. Draw a diagram to show the dispersion of a beam of white light by a glass prism.
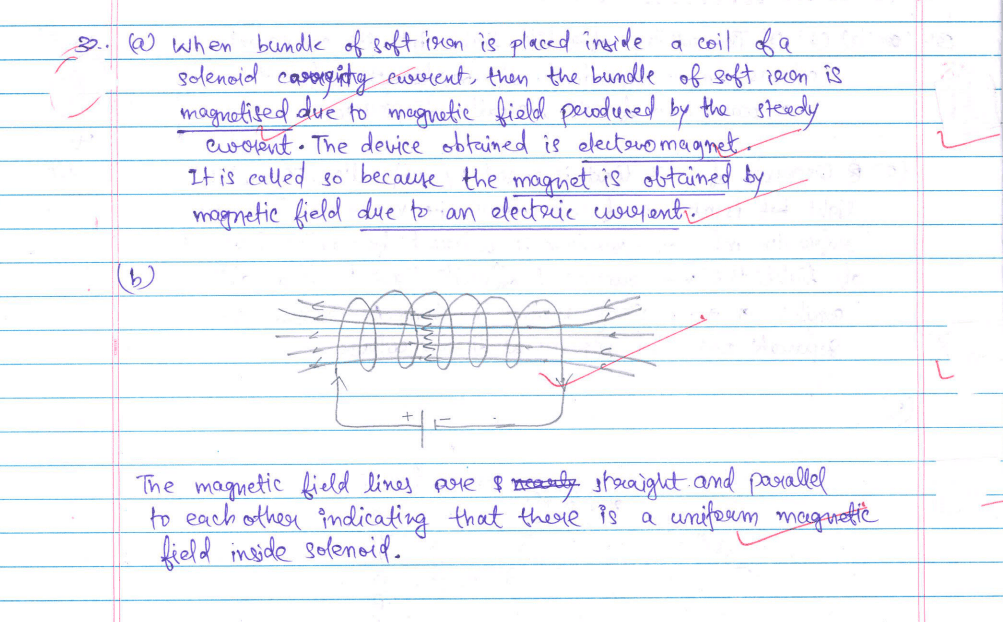
32. (a) What happens when a bundle of wires of soft iron is placed inside the coil of a solenoid carrying a steady current? Name the device obtained. Why is it called so?
(b) Draw the magnetic field lines inside a current-carrying solenoid. What does this pattern of magnetic field lines indicate?
33. Differentiate between food chain and food web. In a food chain consisting of deer, grass, and tiger, if the population of deer decreases, what will happen to the population of organisms belonging to the first and third trophic levels?

SECTION D
Questions no. 34 to 36 are long answer type questions.
34. (a) A few crystals of ferrous sulphate were taken in a dry boiling tube and heated. Tiny water droplets were observed in the tube after some time.
(i) From where did these water droplets appear? Explain.
(ii) What colour change will be observed during heating?
(iii) How many molecules of water are attached per molecule of FeSO₄ crystal? Write the molecular formula of crystalline forms of (I) Copper sulphate, and (II) Sodium carbonate.
(iv) State how is Plaster of Paris obtained from gypsum. Write two uses of Plaster of Paris.
OR
(b) An acid ‘X’ present in tamarind when mixed with ‘Y’, produces a mixture ‘Z’. ‘Z’ on addition to a dough when heated makes cakes soft and spongy. ‘Y’ is prepared from common salt and helps in faster cooking.
(i) Write the common names of ‘X’, ‘Y’, and ‘Z’, and the chemical formula of ‘Y’.
(ii) How is ‘Y’ prepared and how does it help in making cakes soft and spongy? Illustrate the reaction with a suitable chemical equation.
(iii) Write the name and chemical formula of a mild base other than ‘Y’ used as an antacid.



35. (a) Design an experiment to demonstrate that carbon dioxide is essential for photosynthesis. Write the observation and conclusion of the experiment.
OR
(b) (i)
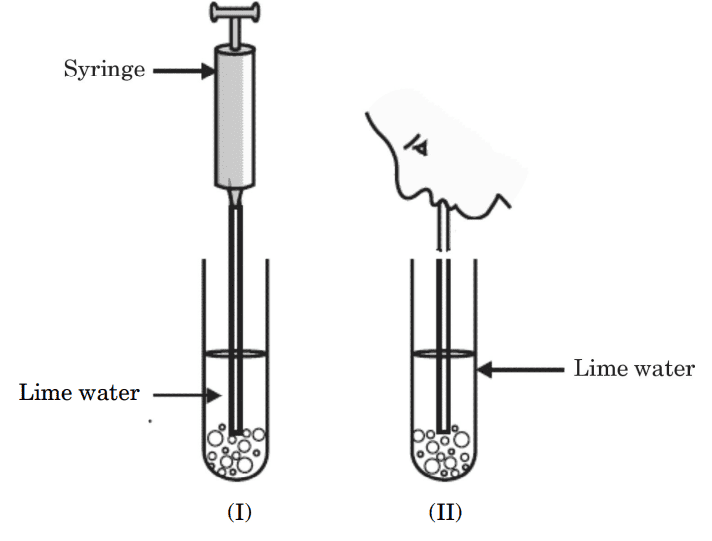
In the experimental set-up shown above in diagram (I), atmospheric air is being passed into lime water with a syringe while in diagram (II), air is being exhaled into lime water. The time taken for the lime water to turn milky in both the test tubes is different. Give reason.
(ii) Draw the diagram of an open stomatal pore and label (I) Guard cells, and (II) Chloroplast on it. Mention two functions performed by stomata.


36. (a) (i) The potential difference across the two ends of a circuit component is decreased to one-third of its initial value, while its resistance remains constant. What change will be observed in the current flowing through it? Name and state the law which helps us to answer this question.
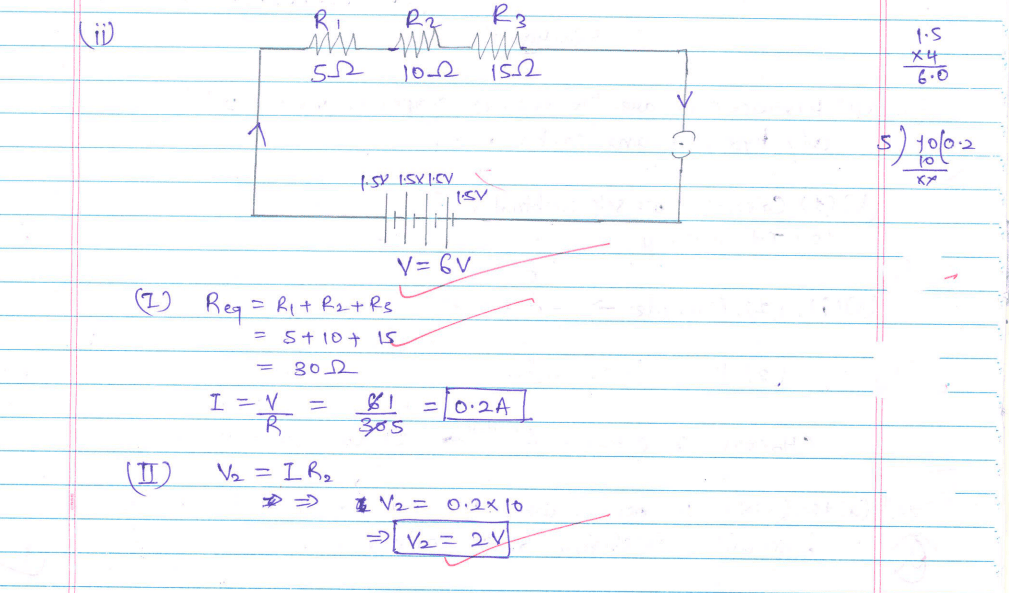
(ii) Draw a schematic diagram of a circuit consisting of a battery of four 1.5 V cells, a 5 Ω resistor, a 10 Ω resistor, and a 15 Ω resistor and a plug key, all connected in series. Now find (I) the electric current passing through the circuit, and (II) potential difference across the 10 Ω resistor when the plug key is closed.
OR
(b) (i) When is the potential difference between two points said to be 1 volt?
(ii) A copper wire has a diameter of 0.2 mm and resistivity of 1·6 x 10-8 Ω m. What will be the length of this wire to make its resistance 14 Ω? How much does the resistance change if the diameter of the wire is doubled?

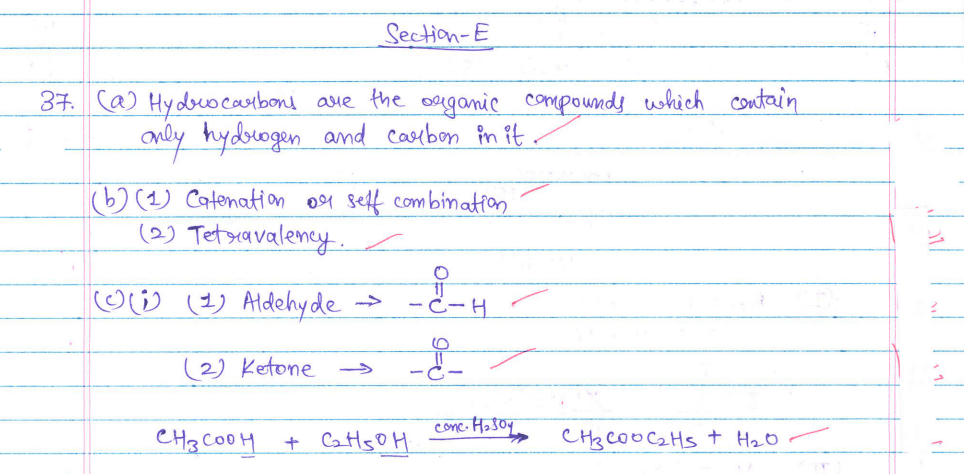
37. Carbon is a versatile element that forms the basis of all living organisms and many of the things we use. A large variety of compounds is formed because of its tetravalency. Compounds of carbon are formed with oxygen, hydrogen, nitrogen, sulphur, chlorine, and many other elements. Answer the following questions:
(a) What are hydrocarbons?
(b) List two properties by virtue of which carbon can form a large number of compounds.
(c) (i) Write the formula of the functional group present in (1) aldehydes, and (2) ketones. Write the chemical equation for the reaction that occurs between ethanoic acid and ethanol in the presence of a catalyst.
OR
(c) (ii) What are structural isomers? Write the structures of two isomers of butane (C4H10).
38. Pollination is an important process in sexual reproduction of plants. It is an essential process that facilitates fertilisation in plants. Pollinating agents can be wind, water, insects, and birds. Several changes take place in the flower after the fertilisation has taken place.
(a) Write the main difference between self-pollination and cross-pollination.
(b) Name the part of the flower which attracts insects for pollination. What happens to this part after fertilisation?
(c) (i) Define fertilisation. What is the fate of ovules and the ovary in a flower after fertilisation?
OR
(c) (ii) In a germinating seed, which parts are known as future shoot and future root? Mention the function of cotyledon.


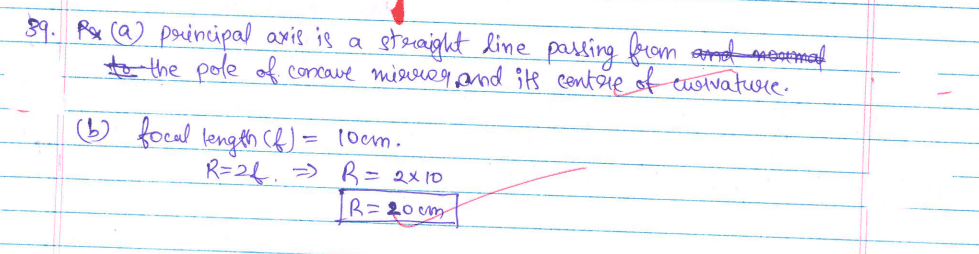
39. A highly polished surface such as a mirror reflects most of the light falling on it. In our daily life, we use two types of mirrors — plane and spherical. The reflecting surface of a spherical mirror may be curved inwards or outwards. In concave mirrors, reflection takes place from the inner surface, while in convex mirrors, reflection takes place from the outer surface.
(a) Define the principal axis of a concave mirror.
(b) A ray of light is incident on a concave mirror, parallel to its principal axis. If this ray after reflection from the mirror passes through the principal axis from a point at a distance of 10 cm from the pole of the mirror, find the radius of curvature of the mirror.
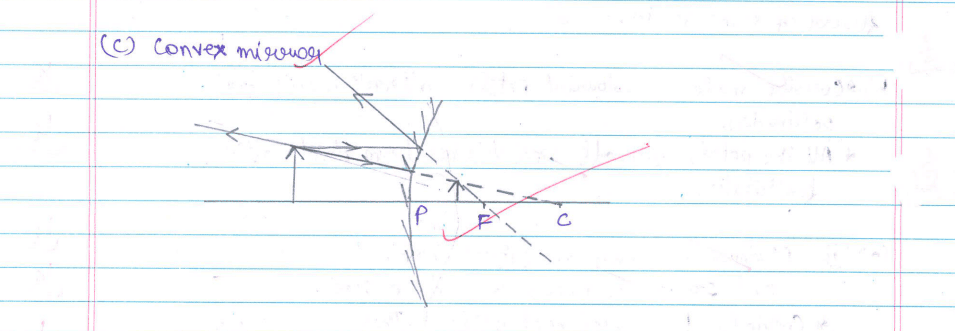
(c) (i) An object is placed at a distance of 10 cm from the pole of a convex mirror of focal length 15 cm. Find the position of the image.
OR
(c) (ii) A mirror forms a virtual, erect, and diminished image of an object. Identify the type of this mirror. Draw a ray diagram to show the image formation in this case.
Additional Resources for CBSE Class 10 Science 2025
🔹 CBSE Class 10 Science Sample Paper 2024-25 – [Click Here]
🔹 NCERT Class 10 Science Important Questions – [Click Here]
🔹 CBSE Science Chapter-wise Revision Notes – [Click Here]
Final Tips for CBSE Class 10 Science Exam 2025
🔹 Stick to NCERT concepts and avoid unnecessary extra materials.
🔹 Revise previous years’ question papers (which I have already included in the important questions answers) to understand the exam pattern.
🔹 Attempt mock tests/revision to improve speed and accuracy.
🔹 Use scientific language while writing answers to impress examiners.
By following these strategies and learning from the CBSE Class 10 Science 2024 topper’s answer sheet, you can improve your answer presentation and boost your scores in the board exams!
Stay tuned for more CBSE Class 10 Science study resources! Let us know in the comments if you found this helpful. 😊
Download Topper's Answer Sheet PDF
🔔 Follow us for More CBSE Updates
📌 Subscribe to Our YouTube Channel: CBSE Guidance
I want 100%in board exam in2025 so Iam doing the hardwork ❤️
Nice
Please board questions paper science
Tomorrow is my class 10th board exam how many marks did I got