Acids, bases, and salts are fundamental concepts in Class 10 Chemistry Chapter 2, and understanding them is essential for success in Class 10 exams. These notes provide a comprehensive overview of the properties, reactions, and uses of acids, bases, and salts, as well as key definitions and equations to help you ace your exams. You can also download the pdf by using the options given below.

| Subject | Science (Chemistry) |
| Class | 10 |
| Board | CBSE & State Boards |
| Chapter No. | 2 |
| Chapter Name | Acids, Bases, and Salts |
| Type | Notes pdf |
| Session | 2024-25 |
"The harder you work for something, the greater you'll feel when you achieve it."
- Unknown
Table of Contents
Acids, Bases, and Salts Class 10 Notes pdf
| Acids | Bases |
| 1. Sour in taste. | 1. Bitter in taste. |
| 2. Change the color of the blue litmus to red. | 2. Change the color of the red litmus to blue. |
Acid-Base Indicators:
- Natural Indicators: Litmus, turmeric, red cabbage leaves, turmeric, colored petals of some flowers such as Hydrangea, Petunia, and Geranium.
- Synthetic Indicators: Methyl orange, phenolphthalein, etc.
Note: A stain of curry on a white cloth becomes reddish-brown when soap, which is basic in nature, is scrubbed on it.
Chemical Properties of Acids and Bases
1.Acids and Bases in the Laboratory
Indicators changing color
| Red litmus solution | Blue litmus solution | Phenolphthalein solution | Methylorgane solution |
| Acid - No change Base - Blue | Acid - Red Base - No change | Acid - Colorless Base - Pink | Acid - Red Base - Yellow |
Olfactory Indicators: There are some substances whose odour changes in acidic or basic media. These are called olfactory indicators. For example vanilla, onion, and clove.
2. How do Acids and Bases react with Metals?
i. Reaction of Acids with Metals:
The metal displaces hydrogen atoms from the acids as hydrogen gas and forms a compound called salt.
Acid + Metal → Salt + Hydrogen gas
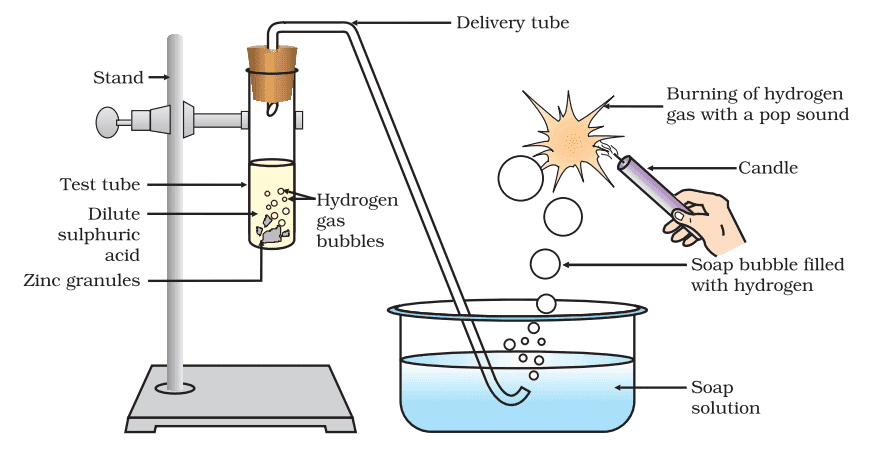
Reaction: Zn + H2SO4 → ZnSO4 + H2↑
ii. Reactions of Bases with Metals:
2NaOH (aq) + Zn (s) → Na2ZnO2 (s) (Sodium zincate) + H2 (g)
3. How do Metal Carbonates and Metal Hydrogencarbonates React with Acids?
All metal carbonates and hydrogen carbonates react with acids to give corresponding salt, carbon dioxide, and water.
Metal carbonate/Metal hydrogen carbonate + Acid → Salt + Carbon dioxide + Water
- Na2CO3 (s) + 2HCl (aq) → 2NaCl (aq) + H2O (l) + CO2 (g)
- NaHCO3 (s) + HCl (aq) → NaCl (aq) + H2O (l) + CO2 (g)
- On passing the carbon dioxide gas evolved through lime water:
Ca(OH)2 (aq) (lime water) + CO2 (g) → CaCO3 (s) (white precipitate) + H2O (l)
- On passing excess carbon dioxide the following reaction takes place:
CaCO3 (s) + H2O (l) + CO2 (g) → Ca(HCO3)2 (aq) (soluble in water)
- Limestone, chalk, and marble are different forms of calcium carbonate.
4. How do Acids and Bases React with each other?
Neutralization Reaction: An acid and a base react with each other to give salt and water. This reaction is known as the Neutralization reaction.
Base + Acid → Salt + Water
NaOH (aq) + HCl (aq) → NaCl (aq) + H2O (l)
5. Reaction of Metallic Oxides with Acids
Metal oxide + Acid → Salt + Water
CuO + HCl → CuCl2 (blue-green) + H2O
Metallic oxides are basic oxides.
6. Reaction of a Non-metallic Oxide with Base
Non-Metal oxide + Base → Salt + Water
CO2 + Ca(OH)2 → CaCO3 + H2O
Non-Metallic oxides are acidic oxides.
What do All Acids and Bases have in Common?
Acids contain H+ ions as cations and anions such as Cl– in HCl, NO3– in HNO3, SO42– in H2SO4, and CH3COO– in CH3COOH. Since the cation present in acids is H+ this suggests that acids produce hydrogen ions, H+ (aq), in solution, which are responsible for their acidic properties.
What Happens to an Acid in a Water Solution?
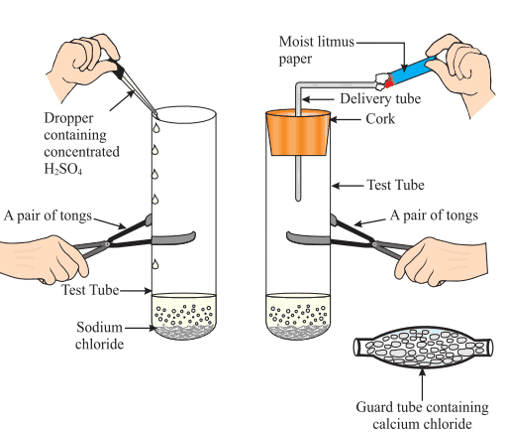
NaCl + H2SO4 → Na2SO4 + HCl
The HCl gas evolved in the above experiment turns moist blue litmus red, but has no effect on dry litmus paper.
This experiment suggests that hydrogen ions in HCl are produced in the presence of water. The separation of H+ ions from HCl molecules cannot occur in the absence of water.
HCl + H2O → H3O+ + Cl–
Hydrogen ions cannot exist alone, but they exist after combining with water molecules. Thus hydrogen ions must always be shown as H+ (aq) or hydronium ions (H3O+).
H+ + H2O → H3O+
What Happens to a Base in a Water Solution?
NaOH(s) + H2O → Na+ (aq) + OH– (aq)
Bases generate hydroxide (OH– ) ions in water. Bases that are soluble in water are called alkalis.
All bases do not dissolve in water. An alkali is a base that dissolves in water.
The acid must always be added slowly to water with constant stirring because:
- The process of dissolving an acid or a base in water is a highly exothermic one.
- If water is added to concentrated sulphuric acid, the heat generated may cause the mixture to splash out and cause burns.
- The glass container may also break due to excessive local heating.
Dilution: Mixing an acid or base with water results in a decrease in the concentration of ions (H3O+/OH– ) per unit volume. Such a process is called dilution.
How Strong Are Acid or Base Solutions?
We can judge the strength of an acid or a base by making use of a universal indicator, which is a mixture of several indicators. The universal indicator shows different colors at different concentrations of hydrogen ions in a solution.
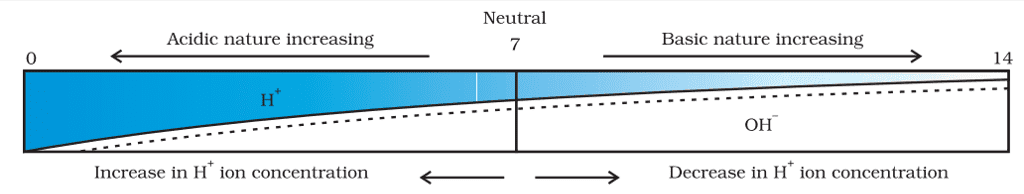
pH Scale
- A scale for measuring hydrogen ion concentration in a solution, called pH scale has been developed.
- The p in pH stands for ‘potenz’ in German, meaning power.
- On the pH scale, we can measure pH generally from 0 (very acidic) to 14 (very alkaline).
- pH should be thought of simply as a number that indicates the acidic or basic nature of a solution.
- The higher the hydronium ion concentration, the lower the pH value.
- The pH of a neutral solution is 7.
- Values less than 7 on the pH scale represent an acidic solution.
- As the pH value increases from 7 to 14, it represents an increase in OH– ion concentration in the solution, that is, an increase in the strength of the alkali.
- Generally, paper impregnated with the universal indicator is used for measuring pH.
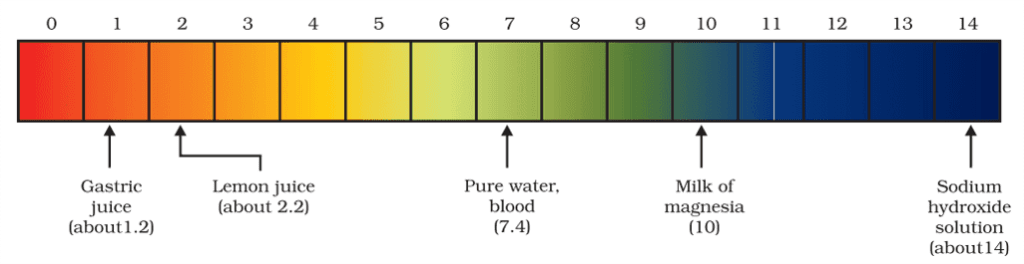
Importance of pH in everyday life
Are plants and animals pH sensitive?
- Our body works within the pH range of 7.0 to 7.8.
- When pH of rainwater is less than 5.6, it is called acid rain.
- When acid rain flows into the rivers, it lowers the pH of the river water. The survival of aquatic life in such rivers becomes difficult.
pH in our digestive system
- It is very interesting to note that our stomach produces hydrochloric acid. It helps in the digestion of food without harming the stomach.
- During indigestion, the stomach produces too much acid and this causes pain and irritation. To get rid of this pain, people use bases called antacids.
- These antacids neutralize the excess acid. Magnesium hydroxide (Milk of magnesia), a mild base, is often used for this purpose.
pH change as the cause of tooth decay
- Tooth decay starts when the pH of the mouth is lower than 5.5.
- Tooth enamel, made up of calcium hydroxyapatite (a crystalline form of calcium phosphate) is the hardest substance in the body.
- Bacteria present in the mouth produce acids by degradation of sugar and food particles remaining in the mouth after eating.
- The best way to prevent this is to clean the mouth after eating food.
- Using toothpaste, which is generally basic, for cleaning the teeth can neutralize the excess acid and prevent tooth decay.
Self-defense by animals and plants through chemical warfare
Bee-sting leaves an acid that causes pain and irritation. The use of a mild base like baking soda on the stung area gives relief. Stinging hair of nettle leaves injects methanoic acid causing burning pain.
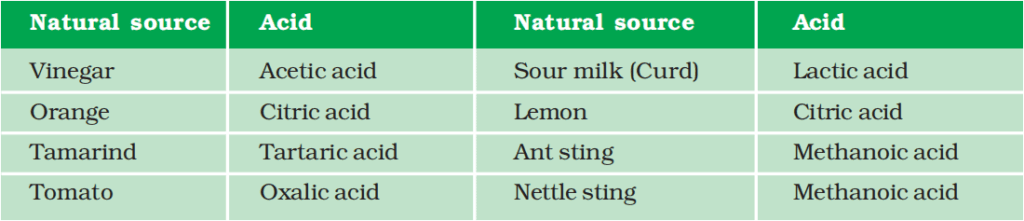
More About Salts
pH of Salts
- Salts of a strong acid and a strong base are neutral with a pH value of 7.
- Salts of a strong acid and weak base are acidic with a pH value of less than 7.
- Those of a strong base and weak acid are basic in nature with a pH value of more than 7.
Chemicals From Commal Salt
The salt formed by the combination of hydrochloric acid and sodium hydroxide solution is called sodium chloride (NaCl)/Common Salt.
The common salt thus obtained is an important raw material for various materials of daily use, such as sodium hydroxide, baking soda, washing soda, bleaching powder, and many more.
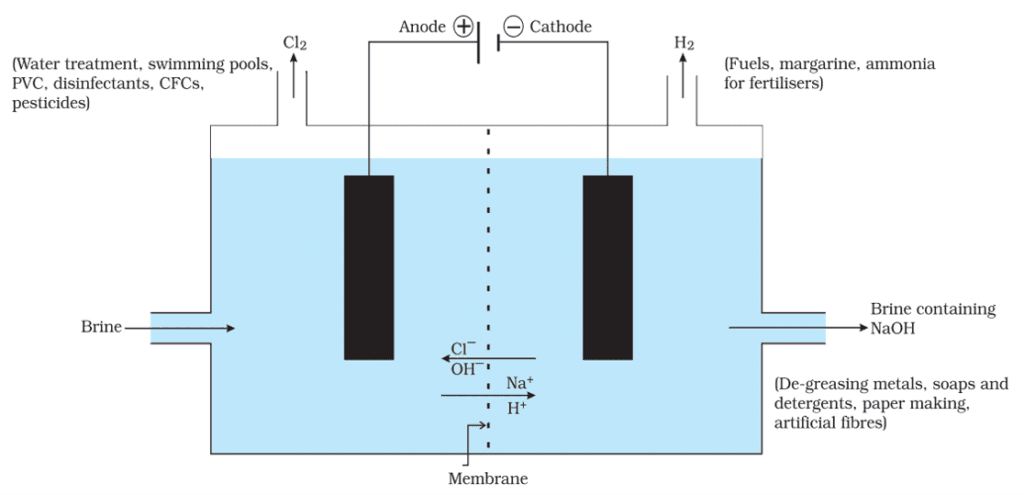
1.Sodium Hydroxide
- When electricity is passed through an aqueous solution of sodium chloride (called brine), it decomposes to form sodium hydroxide. The process is called the chlor-alkali process because of the products formed– chlor for chlorine and alkali for sodium hydroxide.
- 2NaCl (aq) + 2H2O (l) → 2NaOH (aq) + Cl2 (g) + H2 (g)
- Chlorine gas is given off at the anode, and hydrogen gas at the cathode. Sodium hydroxide solution is formed near the cathode.
Bleaching Powder
- Chlorine gas is used for the manufacture of bleaching powder.
- Bleaching powder is produced by the action of chlorine on dry slaked lime [Ca(OH)2].
- Bleaching powder is represented as CaOCl2, though the actual composition is quite complex.
- Ca(OH)2 + Cl2 → CaOCl2 + H2O
Bleaching powder is used –
- for bleaching cotton and linen in the textile industry, for bleaching wood pulp in paper factories, and for bleaching washed clothes in laundry;
- as an oxidizing agent in many chemical industries; and
- to make drinking water free from germs.
Baking Soda
- The chemical name of the compound is sodium hydrogen carbonate (NaHCO3).
- It is produced using sodium chloride as one of the raw materials.
- NaCl + H2O + CO2 + NH3 → NH4Cl + NaHCO3
- It is a mild non-corrosive basic salt.
- The following reaction takes place when it is heated during cooking
- 2NaHCO3 → Na2CO3 + H2O+CO2
Uses of Baking Soda
- For making baking powder, which is a mixture of baking soda (sodium hydrogen carbonate) and a mild edible acid such as tartaric acid.
- Carbon dioxide produced during the heating of baking powder can cause bread or cake to rise making them soft and spongy.
- Sodium hydrogen carbonate is also an ingredient in antacids. Being alkaline, it neutralizes excess acid in the stomach and provides relief.
- It is also used in soda-acid fire extinguishers.
Washing Soda
- It is Na2CO3.10H2O.
Uses of washing soda
- Sodium carbonate (washing soda) is used in the glass, soap, and paper industries.
- It is used in the manufacture of sodium compounds such as borax.
- Sodium carbonate can be used as a cleaning agent for domestic purposes.
- It is used for removing the permanent hardness of the water.
Water of Crystallization
The water of crystallization is the fixed number of water molecules present in one formula unit of salt. Five water molecules are present in one formula unit of copper sulphate. The chemical formula for hydrated copper sulphate is CuSO4.5H2O.
Plaster of Paris
On heating gypsum (CaSO4.2H2O) at 373 K, it loses water molecules and becomes calcium sulphate hemihydrate (CaSO4.1/2H2O). This is called Plaster of Paris.
Uses of Plaster of Paris
- The substance is used by doctors as plaster for supporting fractured bones in the right position.
- Plaster of Paris is used for making toys, materials for decoration, and making surfaces smooth.
| Must Read: Acids, Bases and Salts Class 10 Important Questions & Answers to get an idea of the different types of questions asked from this chapter. |
| You Might Also Like: CBSE Class 10 Notes CBSE Class 10 Important Questions and Answers |
Hope you liked these notes on Class 10 Science Chapter 2 Acids, Bases, and Salts. Please share this with your friends and do comment if you have any doubts/suggestions to share.
Sir wo blue limtus – acid mein red hota h naki base mein uppar galat h likha hua
Haa wo galat tha. Ab thik kar diye. Thanks for telling me.
Sir this notes was very helpful for me thank God I couldn’t find the appropriate notes but this website was having very good notes and I got 89 percentile in 10th its all thank to you and ur notes
1% se 90 ke line se bahar ho gaye 😢
Notice is very nice
Most welcome!
Sir please give notes for 3rd chapter.
Dear Sir,
All your notes are awesome
Thanks a lot for helping me understand the topics so well
Sir preboards going on please upload all science topics
Thanks a lot sir
sir how to access these notes pdf?
How to Download PDF from CBSE Guidance Website
https://youtu.be/zjocgf0LzUM
I got 80% in science by help of this notes. It’s really awesome! . Thank u for this wonderful notes.
Mineral acid and organic acid explain kyu nahi Kiya
notes are so beautiful so elegant just looking like a wow he prabhu he hariram krishna jagganatham he kya hua aeeeee iss notes ke aage koi bol sakta he kya .com moye moye